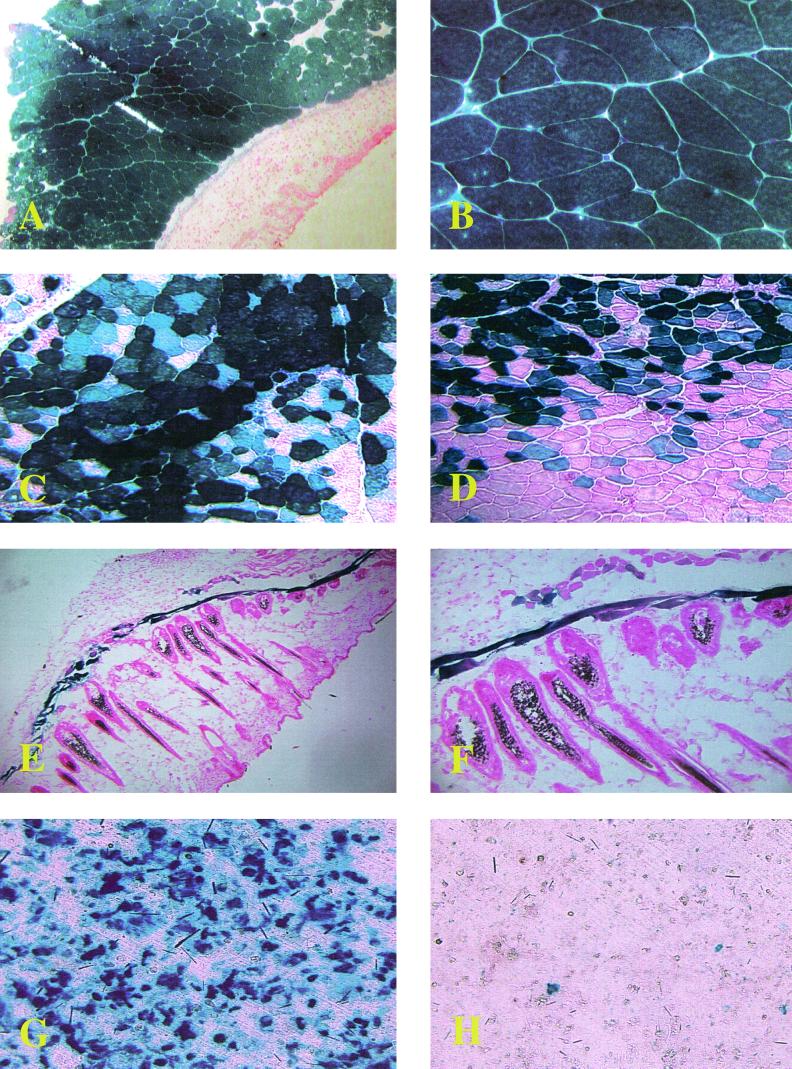
FIG. 1.
AAV5-based cytomegalovirus (CMV) lacZ was derived from plasmid pAAV5 Rn (6), while the AAV5 packaging construct pack 5 was derived from viral AAV5 DNA (3). The hybrid packaging construct pack 2/5 was created by exchanging AAV2 cap from the AAV2 packaging construct p600 trans (2) with AAV5 cap. The AAV2-based AAV CMV lacZ construct has been described previously (2). (A) Transduction of murine muscle with AAV5 CMV lacZ. The right anterior tibialis of C57BL/6 mice was injected with 1010 genome copies of AAV5 CMV lacZ and harvested 28 days postinjection. (B) Higher magnification of panel A. (C and D) Transduction of murine muscle with AAV2/5 CMV lacZ (C) and AAV2 CMV lacZ (D). The right anterior tibialis muscle of C57BL/6 mice was injected with 4 × 1010 genome copies of AAV2/5 CMV lacZ and AAV2 CMV lacZ, respectively. Muscles were harvested 60 days postinjection. (E) Transduction of murine smooth muscle with AAV2/5 CMV lacZ. We injected 1010 genome copies of AAV2/5 CMV lacZ subcutaneously into C57BL/6 mice. Expression of β-gal was assessed 60 days after vector administration. (F) Higher magnification of panel E. (G and H) Apical transduction of primary human epithelial airway cells with AAV2/5 (G) and AAV2CMV (H). Primary human airway epithelial cells were infected apically with 5 × 1010 genomic particles of the corresponding virus (liquid-air transwell system). Cells were fixed and stained with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (X-Gal) 7 days postinfection.