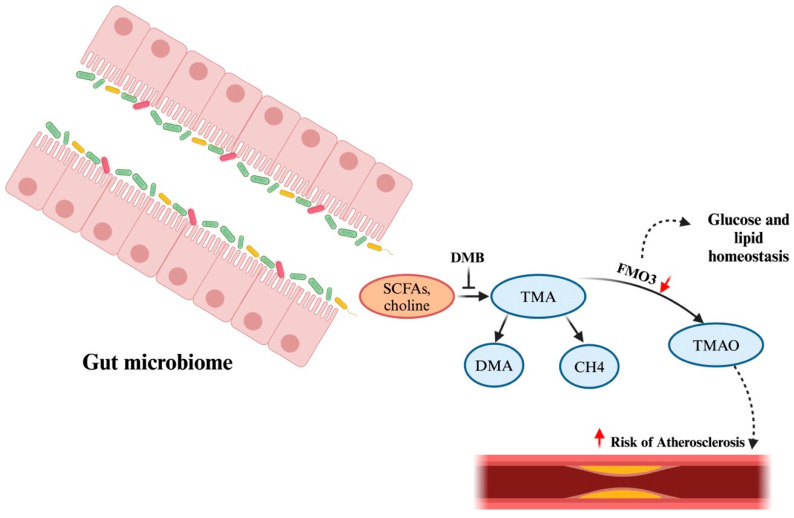
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of gut microbiome converting ingested food into metabolites like short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), choline, and carnitine, which is metabolised into TMA (Trimethylamine), and some part of it is converted into CH4 and DMA + formaldehyde. However, DMB is known to be a repressor of this conversion. TMA is further converted into FMO3 and TMAO after being transported to the liver via the portal vein. Any suppression or deletion in FMO3 leads to altered cholesterol uptake in the intestine and reverse transportation, which might increase the chances of atherosclerosis. This figure was generated using BioRender (www.biorender.com; accessed on 3 May 2024). Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO). The upwards red arrow (↑) represents “increase” and the downwards red arrow (↓) represents “decrease”.