Figure 3.
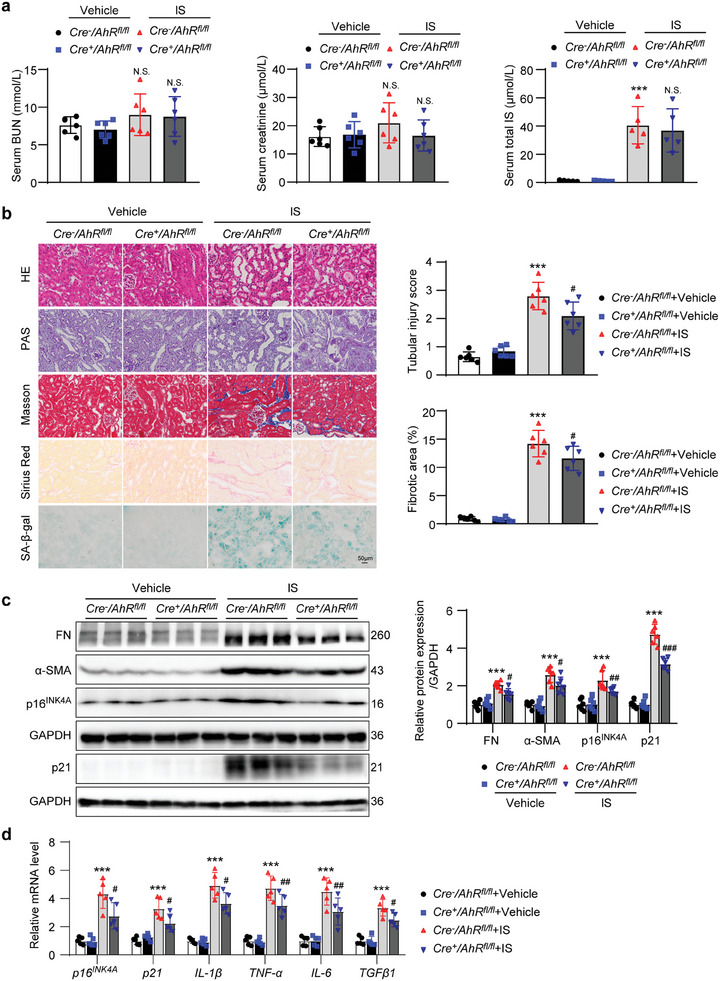
Renal tubular epithelial cell‐specific knockout of AhR mitigated the decline in renal function, senescence and fibrosis in IS‐treated mice. a) Serum BUN, creatinine and IS concentration in different groups of mice. *** P < 0.001 versus Cre−AhRfl/fl +vehicle group. N.S., no significant difference versus Cre−AhRfl/fl +vehicle group or Cre−AhRfl/fl +IS group (n = 5 or 6). b) HE, PAS, Masson, Sirius red and SA‐β‐gal staining micrographs of kidneys from different groups of mice. Scale bar, 50 µm. Evaluation of tubular injury score based on HE staining. Fibrotic area evaluation based on Masson staining. *** P < 0.001 versus Cre−AhRfl/fl +vehicle group, # P < 0.05 versus Cre−AhRfl/fl +IS group (n = 6). c) Western blot images and quantitative data showing FN, α‐SMA, p16INK4A, and p21 in kidneys from different groups of mice. *** P < 0.001 versus Cre−AhRfl/fl +vehicle group, # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, ### P < 0.001 versus Cre−AhRfl/fl +IS group (n = 6). d) qPCR showing the mRNA levels of p16INK4A , p21, IL‐1β, TNF‐α, IL‐6, and TGFβ1 in kidneys from different groups of mice. *** P < 0.001 versus Cre−AhRfl/fl +vehicle group, # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01 versus Cre−AhRfl/fl +IS group (n = 5). Data were shown as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed by two‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test (a‐d).
