Figure 11.
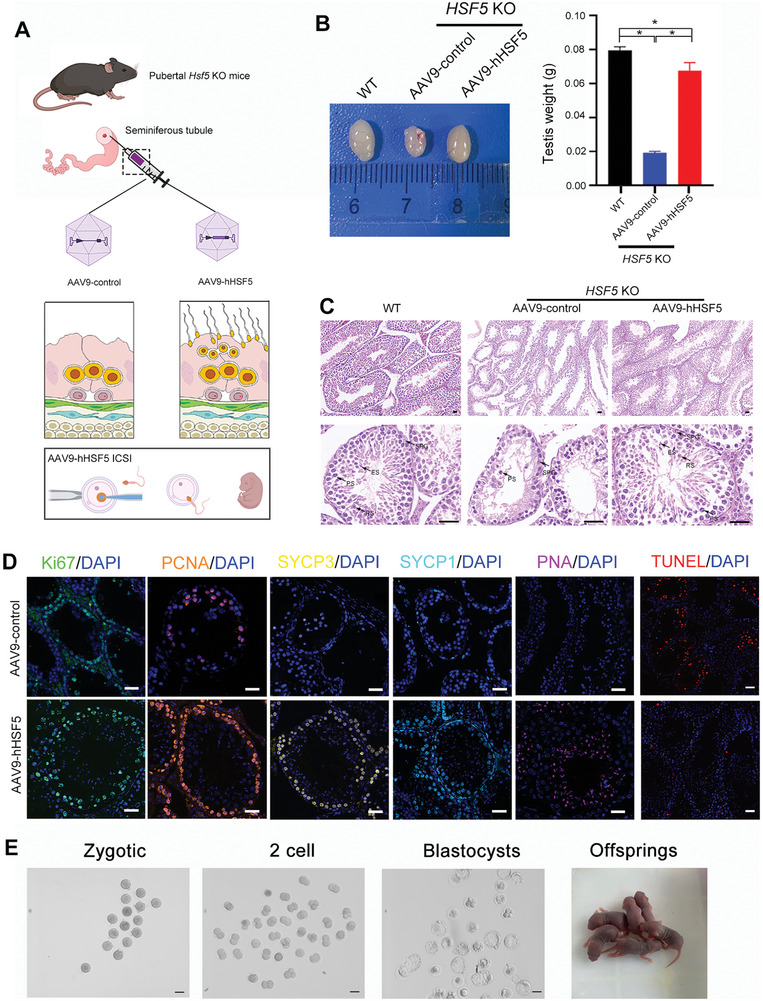
AAV9‐hHSF5 rescues spermatogenesis in Hsf5 KO mice. A) Working model for AAV‐hHSF5‐mediated recovery of spermatogenesis. Created with BioRender.com. B) Macroscopic images and weights of WT and Hsf5 KO mouse testes after microinjection of AAV9‐control (WT and Hsf5 KO respectively) or AAV9‐hHSF5 (Hsf5 KO) (N = 3 biologically independent WT mice and KO mice; two‐sided Student's t test; *P < 0.05; error bars, mean ± SEM). C) Histological analysis of testis sections collected from WT and Hsf5 KO mice injected with AAV9‐control or AAV9‐hHSF5. SPG, spermatogonium; PS, primary spermatocyte; RS, round spermatid; ES, elongating/elongated spermatid (N = 3 biologically independent WT mice and KO mice; scale bars, 125 µm). D) Immunofluorescence staining of signals marking different germ cells and apoptotic cells (N = 3 biologically independent KO mice; blue, DAPI; green, Ki67; orange, PCNA; yellow, SYCP3; sky blue, SYCP1; pink, PNA; red, TUNEL; scale bars, 125 µm). E) Images of one‐cell zygotes, two‐cell embryos, and blastocysts and offspring after ICSI using sperm from AAV9‐hHSF5‐injected Hsf5 KO male mice (N = 3 biologically independent KO mice; scale bars, 100 µm).
