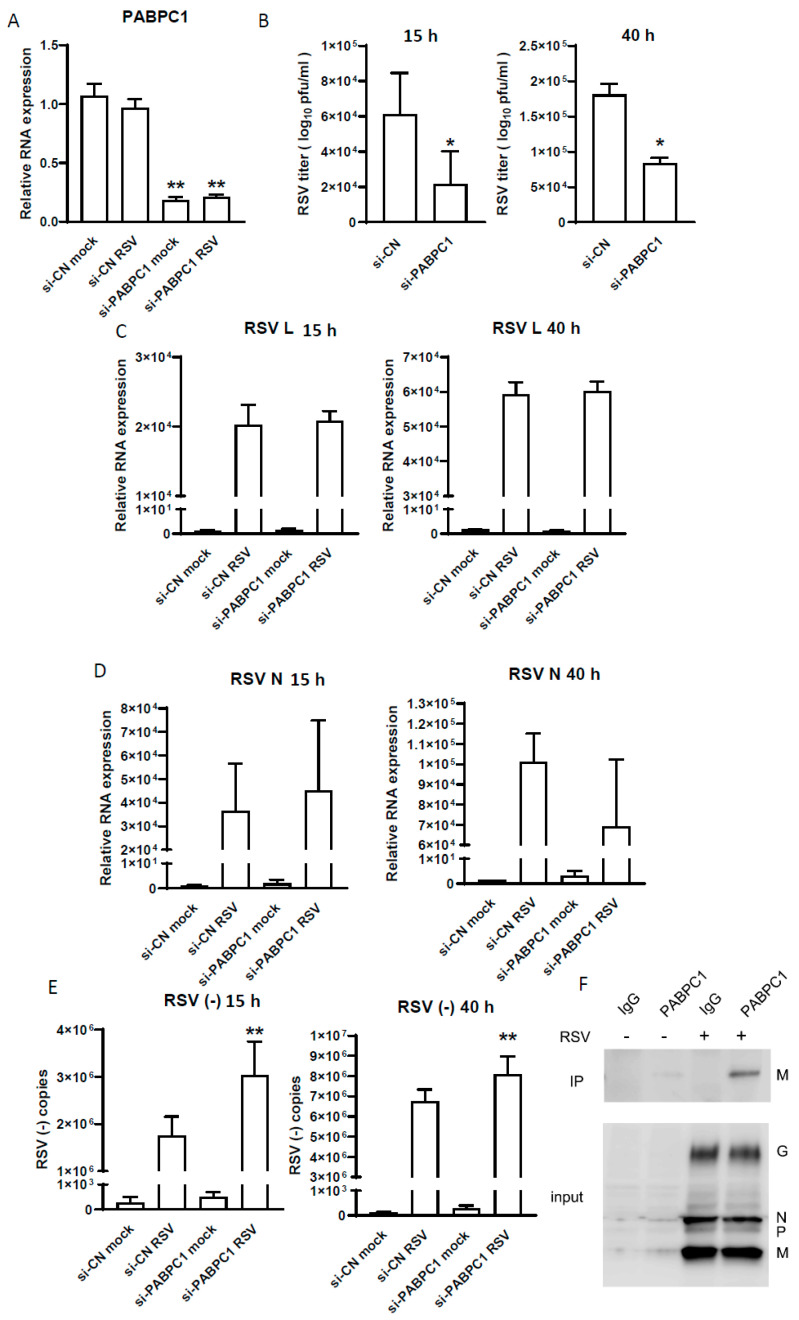
Figure 3.
The impact of PABPC1 on RSV infection. A549 cells were treated with 100 nM of si-PABPC1 or si-cn. At 24 h post-transfection, cells were mock infected or infected with RSV at an MOI of 1. After 2 h of absorption, the inoculation was removed and fresh medium was supplied. Cells were harvested at 15 h or 40 h p.i. for RNA preparation or infectious particle quantification. (A). The knockdown of PABPC1 by its specific siRNAs was confirmed by qRT-PCR. (B) The impact of PABPC1 knockdown on the production of progeny virus. (C,D) The effect of PABPC1 on the expression of RSV long protein L (C) and nucleoprotein N (D). The relative viral gene expression was normalized with β-actin. (E) The impact of PABPC1 on viral genome synthesis. (F) The RSV matrix protein M is present in the PABPC1 pulldown complex. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, compared to the si-CN RSV group.