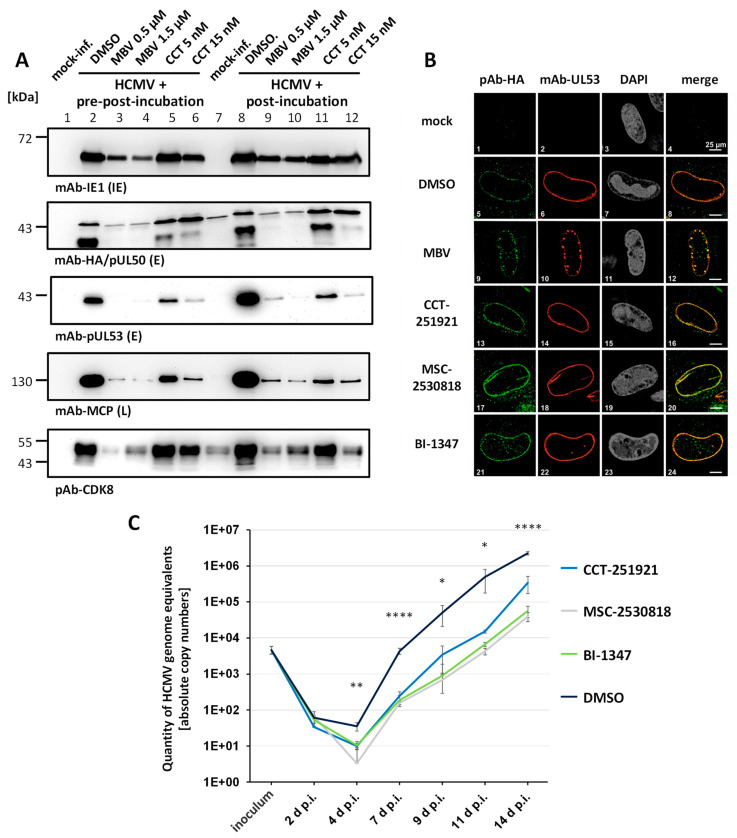
Figure 5.
Mechanistic characteristics of the antiviral activity of CDK8 inhibitors. (A) An analysis of virus entry in the presence of CDK8 inhibitors was performed by comparing pre-post-incubation and post-incubation conditions of drug treatment. HFFs were infected with recombinant HCMV AD169 expressing an HA-tagged pUL50 (AD169-UL50-HA) at MOI of 0.01. For vCDK and CDK8 inhibitor treatments, two different setups were used. One set of cells was treated with MBV (0.5 µM and 1.5 µM) or CCT (5 nM and 15 nM) before, during, and after infection (pre-post). The other set was exclusively treated 90 min after virus absorption (post). Western blot staining was performed for IE1p72, pUL50-HA, pUL53, MCP, and CDK8. (B) The typical nuclear rim localization of viral NEC proteins was analyzed under CDK8 inhibitor treatment. HFFs were cultivated in 6-well plates on cover slips, and used for infection with HCMV AD169-UL50-HA at MOI of 0.05. After 90 min of virus absorption, cells were treated with 0.5 µM MBV, 5 nM CCT, 2 nM MSC, or 0.7 nM BI. Infected cells were fixed at 7 d p.i., and IF staining was performed for viral pUL50-HA and pUL53 to be analyzed by confocal imaging. Counterstaining of the nuclei (DAPI) is indicated, and a merge of pUL50-HA and pUL53 signals is provided on the right. (C) The reduction in virus progeny production and release was quantitated under CDK8 inhibitor treatment. For this purpose, HFFs were infected with AD169-UL50-HA at MOI of 0.01 and treated with 5 nM CCT, 2 nM MSC, 0.7 nM BI, or DMSO in the control. Supernatant samples were taken at 2, 4, 7, 9, 11, and 14 d p.i., to perform virus-specific qPCR analysis. Statistical evaluation was conducted using an ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s correction method for multiple comparison (* p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, **** p ≤ 0.0001).