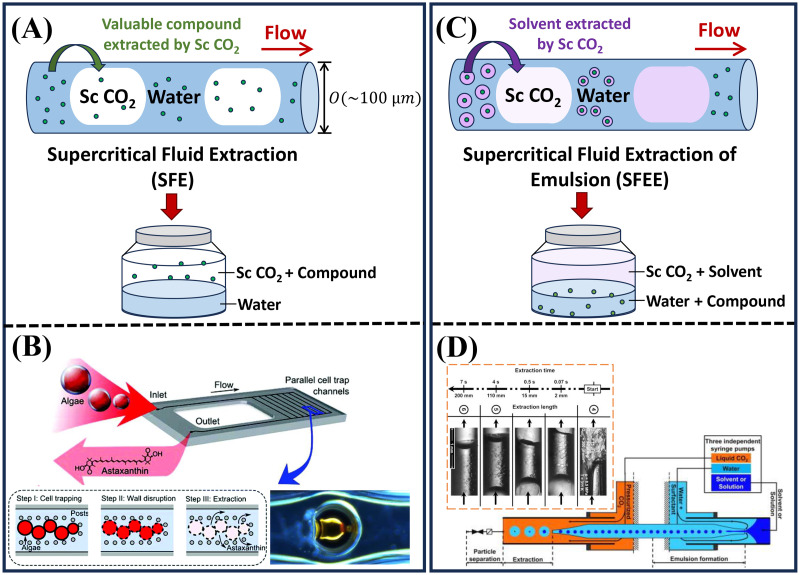
FIG. 3.
Supercritical extraction processes in microfluidics. (a) A schematic illustration of supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) in a microcapillary, where the valuable compound is extracted into the supercritical bubbles. The typical microchannel diameter is of the order of a few hundred m. (b) Supercritical extracts astaxanthin from hydrothermally disrupted algae cells using a silicon-glass microfluidic device.42,67 Reproduced with permission from Cheng et al., Green Chem. 19, 106–111 (2017). Copyright 2017 Royal Society of Chemistry. Reproduced with permission from Cheng et al., Bioresour. Technol. 250, 481-485 (2018). Copyright 2018 Elsevier. (c) A schematic illustration of supercritical fluid extraction of emulsion (SFEE) in a microcapillary, where the supercritical bubbles extract the solvent from the water/solvent/chemical compound mixture. (d) Supercritical extracts an organic solvent, ethyl acetate, from water plus solvent emulsions in a microcapillary.36 Reproduced with permission from Luther and Braeuer, J. Supercrit. Fluids 65, 78–86 (2012). Copyright 2012 Elsevier.