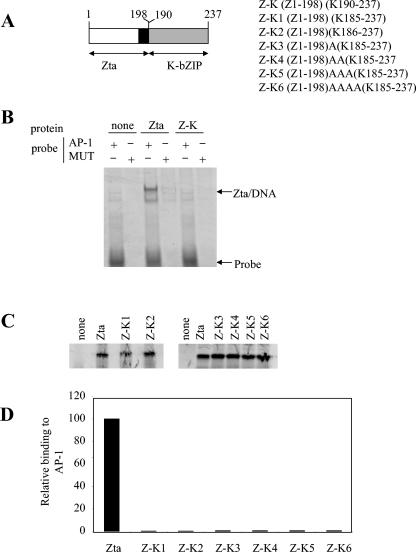
FIG. 2.
K-bZIP domain swap proteins do not function as bZIPs. A. Vectors encoding hybrid proteins composed of the Zta transactivation and basic domains and the K-bZIP putative zipper domain were generated and are shown schematically here. The Zta basic region is shown in black. The region of K-bZIP from the proposed zipper to the carboxy terminus is shown as a grey box. B. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay reactions were undertaken with equal quantities of the indicated proteins and probes (as described in reference 15). Following electrophoresis, the locations of the probe and DNA complexes were visualized using phosphorimaging. C. Products from the indicated translation reactions were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and quantitated by phosphorimaging. The migration of protein molecular weight markers (in kDa) is indicated on the left. D. Following the electrophoretic mobility shift assay analysis with equal amounts of protein, the specific binding of His-Zta and each hybrid protein to DNA is shown.