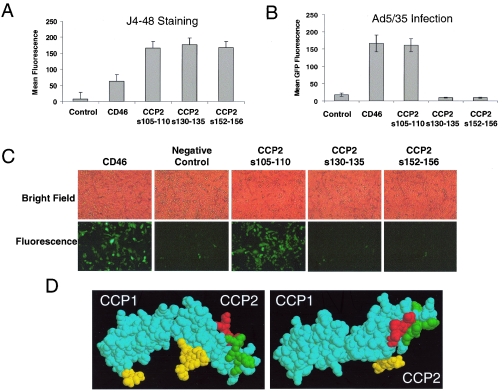
FIG. 7.
Substitutions of amino acid residues 130 to 135 and 152 to 156 in the CCP2 domain completely abolish adenovirus receptor function of CD46. (A) CHO cells were transfected with plasmids expressing either wild-type CD46 (CD46) or full-length CD46 mutants possessing four amino acid substitutions of the indicated amino acids within the CCP2 domain. The levels of CD46 protein expression were determined by J4-48 antibody staining and flow cytometry 48 h posttransfection. (B) Mean GFP fluorescence of CHO cells transfected with plasmids described for panel A and infected with Ad5/35GFP vector. Error bars indicate standard deviations; n = 4. (C) Bright-field and fluorescence photographs of transfected CHO cells 24 h after Ad5/35GFP infection shown in panel B. (D) Crystal structure representation of domains CCP1 and CCP2 of CD46, with residues 96 to 101 shown in green, residues 118 to 122 shown in red, and N-linked glycosylations shown in yellow.