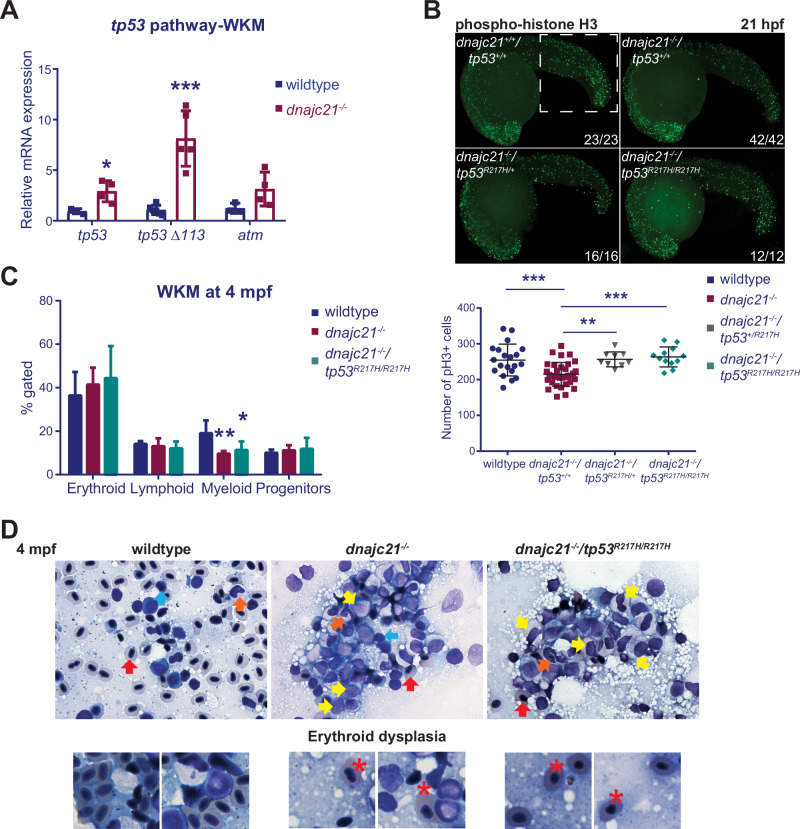
Fig. 4. A gain-of-function tp53 mutation partially rescues neutropenia but leads to an expansion of immature progenitors.
A Levels of tp53, tp53 Δ113 isoform, and atm mRNA measured by qPCR in kidney marrows of wildtype and dnajc21−/− fish at 8 mpf. b-actin and eef1a1l1 were used for normalization. B dnajc21−/− mutants were crossed with tp53R217H/R217H to generate compound mutant dnajc21−/−/tp53R217H/R217H fish. Lateral views of pH3 immunofluorescence in wildtype, dnajc21−/−, dnajc21−/−/tp53R217H/+ and dnajc21−/−/tp53R217H/R217H mutant embryos at 21 hpf. Experiments were done in 2 biological replicates. Numbers on the lower right indicate the number of larvae with the same phenotype. The white dotted box marks the region used for counting. The number of pH3+ cells per embryo is quantified in the graph. C Flow cytometry of kidney marrows from wildtype (n = 5), dnajc21−/− (n = 5) and dnajc21−/−/tp53R217H/R217H (n = 3) fish at 4 mpf. Hematopoietic lineages were detected based on the forward and side scatter profiles. D Representative images from Giemsa staining of kidney marrow touch preparations from wildtype (n = 3), dnajc21−/− (n = 5), and dnajc21−/−/tp53R217H/R217H (n = 4) fish at 4 mpf. Arrows indicate mature erythrocytes (red), lymphocytes (blue), myelocytes (yellow), and mature neutrophils (orange). Red asterisks mark dysplastic erythrocytes. hpf: hours post-fertilization; mpf: months post-fertilization *p < 0.01; **p < 0.001; ***p < 0.0001.