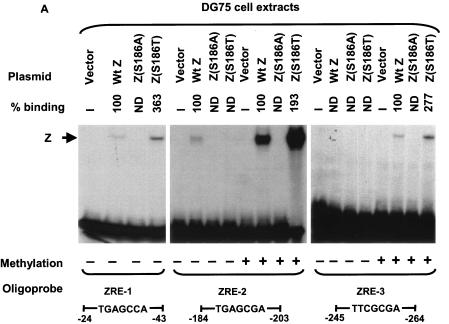
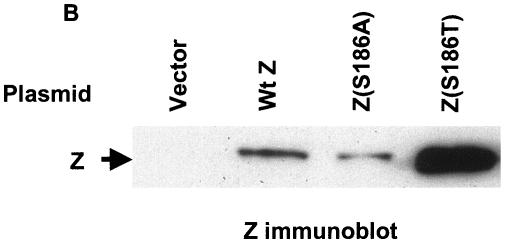
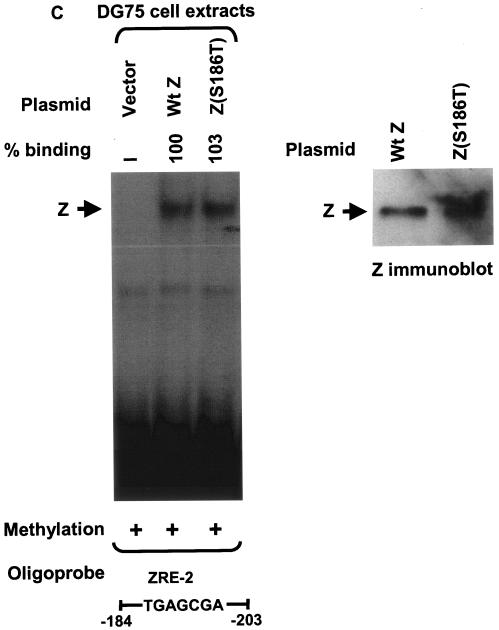
FIG. 4.
Comparison of wild-type Z, Z(S186A), and Z(S186T) binding in transfected DG75 cells extracts. (A) EMSA was performed using either unmethylated or methylated (as indicated) 32P-labeled oligonucleotide probes containing ZRE-1, ZRE-2, or ZRE-3 motifs and whole-cell extracts harvested from DG75 cells transfected with vector DNA or wild-type Z (Wt Z), Z(S186A), or Z(S186T). The binding abilities of mutant Z proteins to each probe were measured relative to wild-type Z, which was set at 100% for each probe. (B) Immunoblot analysis of the whole-cell extracts made from DG75 cells transfected with an empty vector (Vector) or a plasmid expressing wild-type Z, Z(S186A), or Z(S186T) was performed using a monoclonal antibody directed against Z. (C) EMSA was performed using DG75 whole-cell extracts containing normalized levels of wild-type Z and Z(S186T) (as shown in the immunoblot) and 32P-labeled oligonucleotide probe containing methylated ZRE-2. ND, nondetectable binding; +, present; −, absent.