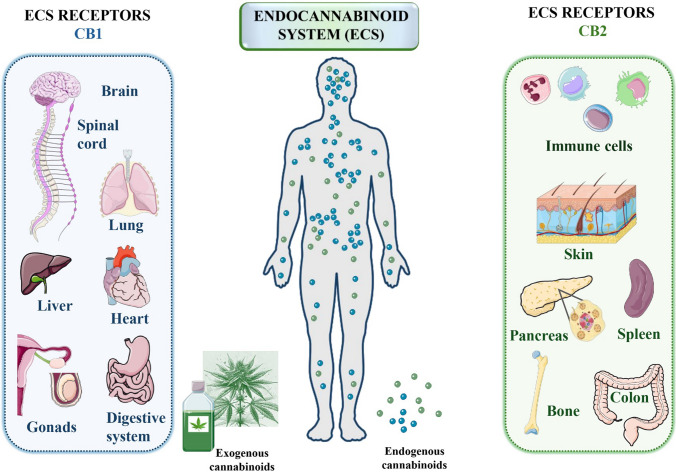
Fig. 3.
Distribution and roles of cannabinoid receptors CB1R and CB2R in the human body. The diagram illustrates the two main types of G-protein coupled cannabinoid receptors: cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2R). CB1R are predominantly found in the brain and spinal cord, where they play vital roles in neurological functions such as synaptic remodeling, neurogenesis, neuron migration, axonal targeting, and synaptogenesis. These receptors are distributed across various regions of the central nervous system, including the hypothalamus, hippocampus, basal ganglia, amygdala, cortex, and cerebellum. In contrast, CB2R are primarily located in the cells and tissues of the immune system, where they significantly modulate immune responses. They are present in immune cells like macrophages in the spleen and tonsils, aiding the immunosuppressive functions of the endocannabinoid system. The diagram emphasizes the specific locations and functions of CB1R and CB2R, highlighting their critical roles in both neurological and immune system processes