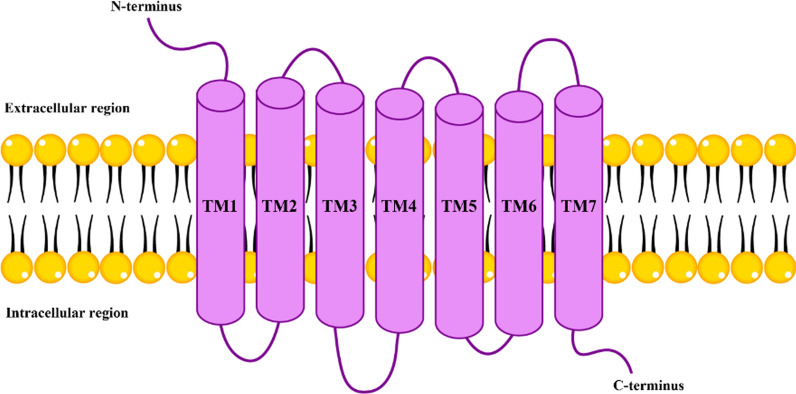
Fig. 4.
Structural model of cannabinoid receptors. This image depicts the structural model of cannabinoid receptors, specifically highlighting the seven transmembrane α-helices (TM1 to TM7). These helices span the cell membrane, forming a bundle that is essential for the receptor’s function. The loops connecting these transmembrane segments extend into both the intracellular and extracellular environments. The receptor features an extracellular N-terminus and an intracellular C-terminus, which includes a short helical segment known as Helix 8. This structural configuration is typical of class A G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), including cannabinoid receptors CB1R and CB2R. These receptors are pivotal in various physiological processes, mediating the effects of endogenous and exogenous cannabinoids by interacting with G proteins and triggering intracellular signaling pathways