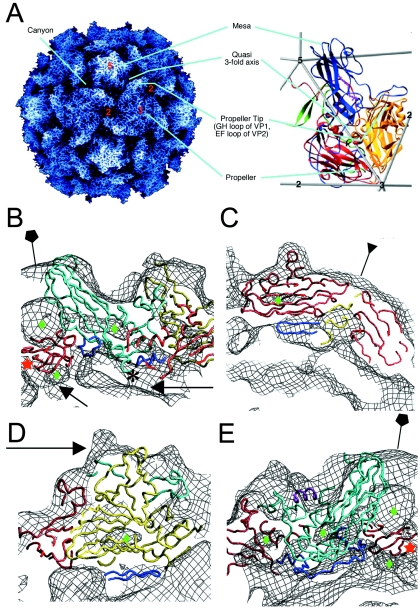
FIG. 3.
Pseudoatomic modeling of the 135S particle. (A) The structure of the 160S particle serves as a reference for prominent structural features. (Left panel) A radially depth-cued rendering of the atomic model (22) of the 160S particle. (Right panel) An expanded representation of a single protomer showing ribbon diagrams of VP1 (blue), VP2 (yellow), VP3 (red), and VP4 (green) overlaid on an icosahedral framework. The fivefold, threefold, and twofold axes are indicated by numbers. Cyan lines point to prominent surface features in the two panels. (B to E) Pseudoatomic models of VP1 (cyan), VP2 (yellow), and VP3 (red) resulting from rigid-body docking and refinement of native virus coordinates into the 135S density maps (black mesh). Residues outside the β-barrel cores that were not modeled previously (3) were included in the refinement (dark blue). Green diamonds signify low-density regions within the core of protein subunits. (B) A model-density overlay in the vicinity of a fivefold axis (pentagon). The RNA and protein shells make contacts (arrows) at the fivefold axis near the VP3 β tube (red star) and at the base of the canyon. The truncated N terminus of VP1 (residue 71) is indicated (*). (C) A model-density overlay in the vicinity of a threefold axis (inverted triangle). Loops at the narrow ends of the VP3 β barrel and the β barrels from symmetry-related VP2s and VP3s alternate around the threefold axis. The newly modeled VP2 β hairpin (dark blue) is seen to contact VP3. (D) Model-density overlay in the vicinity of the propeller tip (arrow) showing VP2, the GH loop and C terminus of VP1 (cyan), and the newly modeled VP2 β hairpin (dark blue) from panel C fitting into a crevice in the EM envelope. (E) A slice through the model-density overlay of a protomer. A helix occupying the external linear ridge, possibly from the residue range 41 to 53 of VP1, is shown in magenta. The newly modeled VP3 N terminus (residues 14 to 49, dark blue) can be seen within the density envelope on the underside of the capsid in panels B and E.