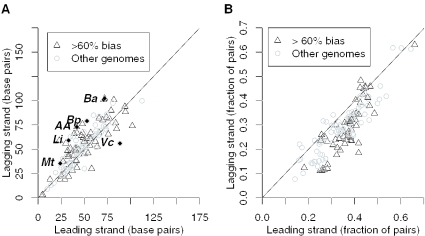
Figure 4.
Across 139 chromosomes from 130 bacteria, adjacent pairs of genes on the leading and lagging strands are separated by similar distances, but pairs on the leading strand are more conserved. (A) The median distance between pairs on the leading strand (x-axis) and the lagging strand (y-axis). (B) The proportion of pairs that are conserved within 5 kb in a distant genome, on both strands (same axes). The lines show x = y. In (A), a few chromosomes do have significantly different distributions of distances on the two strands (false discovery rate < 0.05) and are indicated with labels and filled diamonds: ‘Ba’, Bacillus anthracis Ames strain and Ames ancestor strain; ‘Bp’, Burkholderia pseudomallei K96243 chromosome 2; ‘AA’, Acinetobacter sp. ADP1; ‘Li’, Leptospira interrogans serovar Copenhageni strain Fiocruz L1-130 chromosome 1; ‘Mt’, Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv; and ‘Vc’, Vibrio cholerae chromosome 2. In (B), none of the chromosomes have significantly greater conservation of pairs on the lagging strand (the points above the line are not significantly different from equality, all P > 0.05, Fisher's exact test).