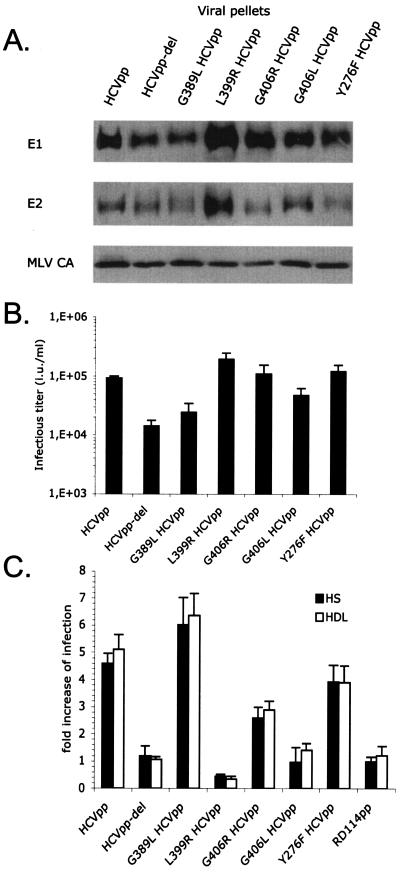
FIG. 3.
Role of HVR1 in facilitation of infection. (A) Immunoblots of purified HCVpp generated with E1 and E2 wild-type or mutant glycoproteins (genotype 1a) are shown. E2 point mutations G389L, L399R, G406R, and G406L are located in the HVR1 region. Y276F HCVpp, an E1 point mutant, served as the control. The HCV glycoproteins and the MLV capsid (MLV CA) proteins were revealed with A4 and H52 monoclonal antibodies against E1 and E2 (9, 13) or with an anti-MLV capsid antiserum (ViroMed Biosafety Laboratories). (B) Titers of HCVpp harboring point mutations. Results are expressed as average infectious titers determined on Huh-7 cells in the absence of serum or lipoproteins (mean ± SD, 3). (C) Results of infection of Huh-7 cells with HCVpp or RD114pp produced in 0.1% FCS, with the addition of 2.5% normal HS or 6 μg/ml HDL to the infection reaction mixture. The concentrations of viral supernatants were adjusted to obtain infection of ca. 5 to 10% of target cells. The results are expressed as ratios between average infectious titers determined in the presence or absence of serum or lipoproteins (mean ± SD, 3).