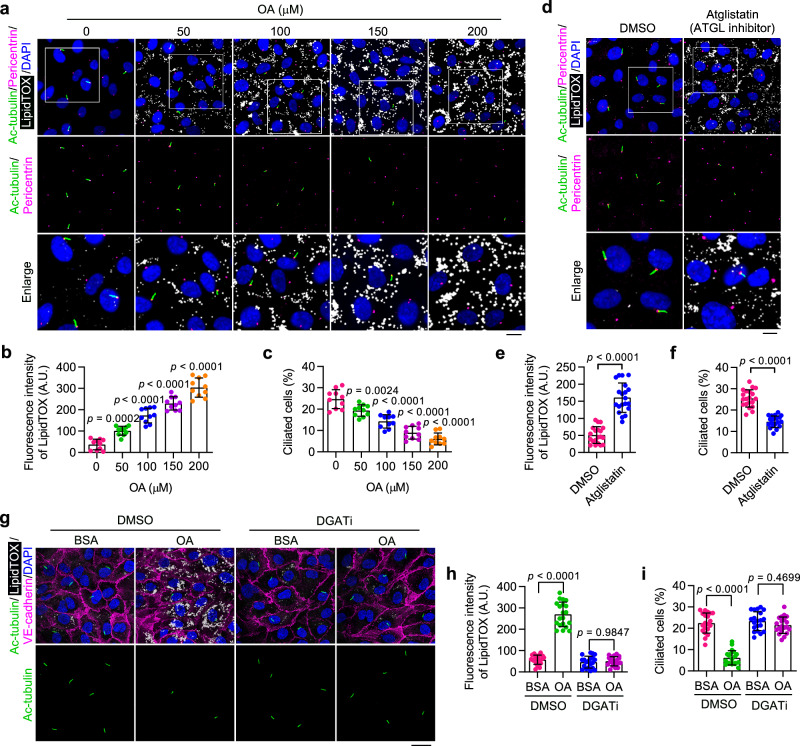
Fig. 2. Accumulation of LDs triggers ciliary loss in cultured VECs.
a–c Immunofluorescence images (a) and quantifications of LipidTOX staining (b) and ciliation (c) of cultured HAECs treated with oleic acid (OA) at the indicated concentration for 12 h, followed by serum starvation for 48 h (n = 10 fields from 3 independent experiments). Boxed areas are enlarged in the bottom panel. Scale bar (for enlarged images), 10 µm. d–f Immunofluorescence images (d) and quantifications of LipidTOX staining (e) and ciliation (f) of HAECs treated with ATGL inhibitor (Atglistatin, 10 µM) for 12 h, followed by serum starvation for 48 h (n = 20 fields from 3 independent experiments). Boxed areas are enlarged in the bottom panel. Scale bar (for enlarged images), 10 µm. g–i Immunofluorescence images (g) and quantifications of LipidTOX staining (h) and ciliation (i) of HAECs treated with DMSO or DGAT inhibitors (A922500, 10 µM and PF-06424439, 5 µM) for 24 h, exposed to bovine serum albumin (BSA) or OA for 12 h, and then serum-starved for 48 h (n = 20 fields from 3 independent experiments). 200 µM OA was used to stimulate LD formation. BSA was used as a control treatment. Scale bar, 20 µm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (e, f), one-way (b, c), or two-way (h, i) ANOVA with post hoc analysis. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.