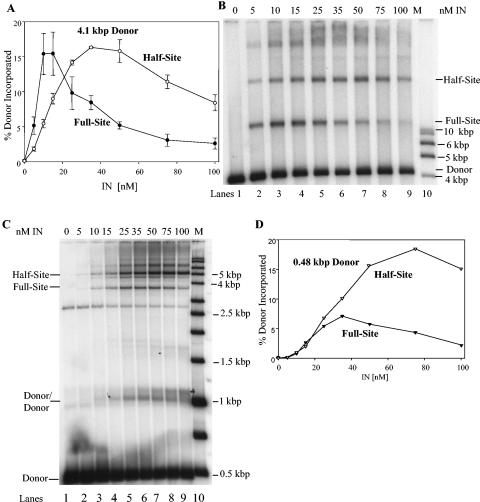
FIG. 2.
Strand transfer activities of recombinant HIV-1 IN under different assay conditions. (A) IN was assembled at 0, 5, 10, 15, 25, 35, 50, 75, and 100 nM with either 32P-labeled 4.1-kbp or 0.48-kbp donors. The 4.1-kbp donor was assembled with IN for 15 min at 14°C prior to strand transfer for 60 min at 37°C. The 0.48-kbp donor (P2) was assembled with IN for 20 min on ice with DMSO prior to strand transfer for 20 min at 37°C (46). The samples were subjected to 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. The dried gels were analyzed by a PhosphorImager, and the percentage of donor incorporated into the integration products was determined from gels shown in panels B and C below. The full-site and half-site products using the 4.1-kbp donors (dark or open circles, respectively) were determined as marked on the figure. The presented data for the 4.1-kbp donor represent triplet measurements with error bar analysis. (B) The full-site and half-site products using the 4.1-kbp donor at various IN concentrations (top) as quantified in panel A. The products and the input donor are indicated on the right. The lane marked “M” on the right contains molecular weight markers as indicated on the right. (C) Same as panel B, except the 0.48-kbp donor was used. The donors/donor products are also shown on the left (46). A nonspecific DNA fragment was present in this P2 DNA preparation that is located in all lanes and migrates just above the 2.5-kbp marker. (D) The percentages of donor incorporated into half-site and full-site products were determined from the data in panel C with the 0.48-kbp donor.