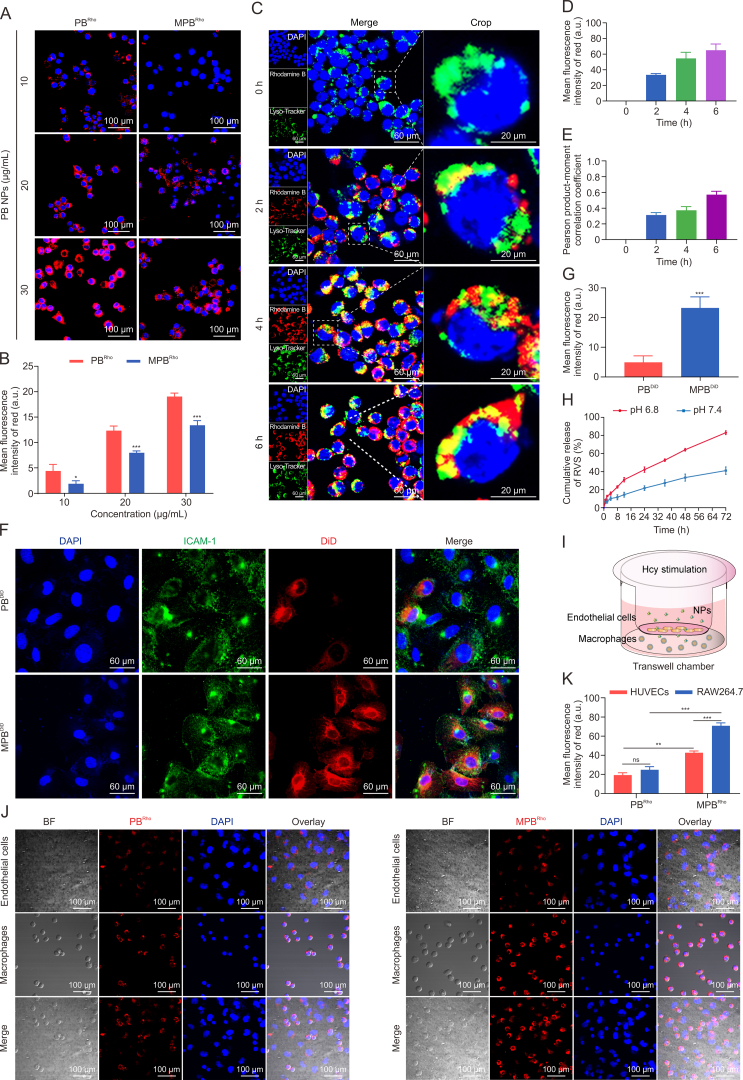
Fig. 2.
Uptake and target ability evaluation of macrophage membrane (Møm)-coated Prussian blue (PB) nanoparticles (MPB NPs) to homocysteine (Hcy)-induced macrophages. (A) Fluorescence images of the immune evading ability of rhodamine B-labeled PB (PBRho) NPs and rhodamine B-labeled Møm-coated PB (MPBRho) NPs. (B) Quantification of rhodamine B fluorescence intensity. (C) Confocal fluorescence microscopy imaging of cells uptake ability and subcellular localization of MPB NPs for different times. (D, E) Quantification of red fluorescence intensity (D) and pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (E) between rhodamine B and Lyso-Tracker fluorescence. (F) Representative fluorescence images of Hcy treated endothelial cells incubating with 1,1-dioctadecyl-3,3,3,3-tetramethylindodicarbocyanine perchlorate (DiD)-labeled PB (PBDiD) NPs and DiD-labeled MPB (MPBDiD) NPs for 24 h. (G) Quantification of DiD fluorescence intensity. (H) The cumulative release of RVS from MPR NPs at different pH values. (I) Schematic diagram of transwell model. (J) Phagocytosis of fluorescent PBRho NPs and MPBRho NPs in co-cultured macrophages and endothelial cells in transwell chambers. (K) Quantitative of rhodamine B fluorescence intensity in macrophages and endothelial cells. Data are means ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 3). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. the PBRho/PBDiD. ns: no significance. DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; PCCs: Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient analysis; BF: bright field; HUVEC: human umbilical vein endothelial cell line.