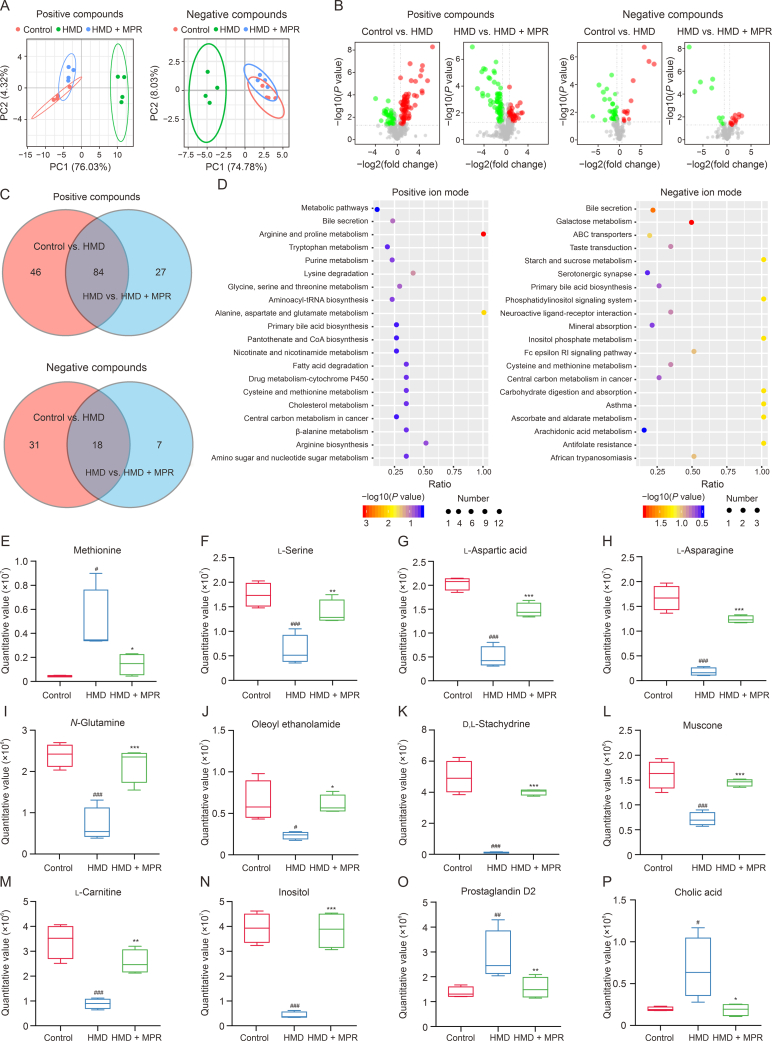
Fig. 8.
Macrophage membrane (Møm)-coated rosuvastatin (RVS)-loaded Prussian blue (PB) nanoparticles (MPR NPs) ameliorates the disorder of metabolite levels caused by high methionine diet (HMD). (A) Principal component analysis (PCA) of the control, HMD, and MPR groups in positive compounds and negative compounds modes. (B) Volcano plot analysis of differential metabolites between the control vs. HMD groups and HMD vs. HMD + MPR groups under positive compounds and negative compounds. Red and green represent upregulated and downregulated metabolites, respectively. (C) Venn gram shows co-expression metabolites between the control vs. HMD and HMD vs. HMD + MPR groups in both positive compounds and negative compounds. (D) Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway involved in differential metabolites between the control, HMD, and MPR groups under positive iron mode and negative iron mode. (E–P) Box chart shows the methionine (E), l-serine (F), l-aspartic acid (G), l-asparagine (H), N-glutamine (I), oleoyl ethanolamide (J), d,l-stachydrine (K), muscone (L), l-carnitine (M), inositol (N), prostaglandin D2 (O), and cholic acid (P) quantitative values in the control, HMD, and HMD + MPR groups. Data are means ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 4). #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001 vs. the control group; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. the HMD. PC: principal component; tRNA: transfer RNA; ABC: adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette transporter; Fc: fragment crystallizable; RI: receptor for immunoglobulin E.