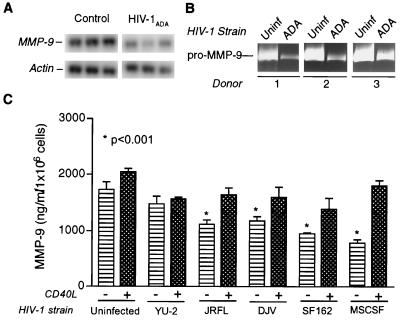
FIG. 5.
Regulation of MMP expression in HIV-1-infected MDM. (A) Adherent monolayers of MDMs were maintained for 7 days prior to infection with HIV-1ADA. Triplicate wells of infected or uninfected control cells had complete medium exchange at day 5 postinfection. Cells were maintained for an additional 48 h. MDMs were harvested in TRIzol, and total RNA was extracted. MMP mRNA was detected by RT-PCR. Representative data for MMP-9 mRNA are shown. Actin was utilized as the internal standard for semiquantitative comparison. HIV-1ADA significantly down-regulated the levels of MMP-9 mRNA (A, ∗, P < 0.05). (B) MDMs were infected as described for panel A. MMP levels in culture supernatant samples from HIV-1-infected and uninfected cells were analyzed by zymography. Culture supernatant volumes were normalized on the basis of endpoint MTT activity. Three independent donors are represented. (C) Secretory profiles of MMP-9 in culture supernatant samples derived from uninfected and HIV-1-infected cells with or without CD40L stimulation were analyzed by ELISA. Three CNS HIV-1 isolates (HIV-1YU-2, HIV-1DJV, and HIV-1JR-FL) and two cerebrospinal fluid HIV-1 isolates (HIV-1SF162 and HIV-1MSCSF) were utilized. All isolates except for HIV-1YU-2 led to a significant down-regulation in MMP-9 levels in infected cells (∗, P < 0.001). CD40L stimulation led to a statistically significant upregulation in MMP-9 levels in uninfected and HIV-1-infected cells, with the exception of HIV-1YU-2 (P < 0.01). Statistical analysis was performed with GraphPad Prism 2.0, using one-way ANOVA with Newman-Keuls posttest.