Fig. 2.
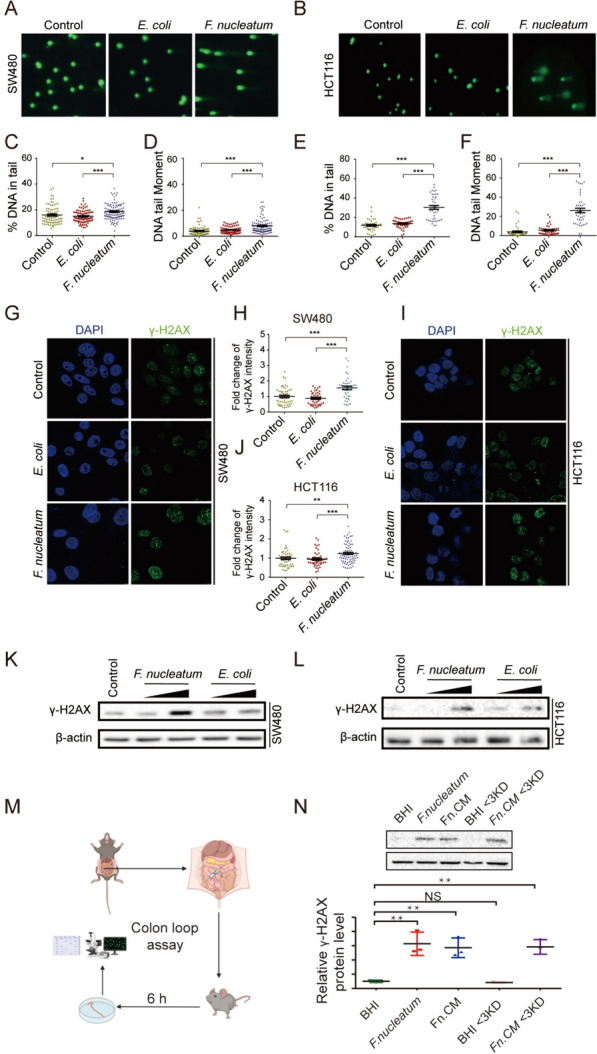
Exposure to F. nucleatum induces host DNA DSBs. Colon cancer cell lines SW480 and HCT116 were exposed to F. nucleatum (MOI = 50) or E. coli (MOI = 100) for 4 h per day under anaerobic conditions for 3 consecutive days. Cell lines SW480 and HCT116 were then harvested and subjected in neutral comet assay A, B and DSBs were quantified by DNA in tail C, E and DNA tail moment D, F γ-H2AX immunofluorescence stain was visualized by the confocal images of γ-H2AX (green) and DNA (blue) in cell line SW480 G and cell line HCT116 (I). H, J Fold change of γ-H2AX were compared by Wilcoxon rank-sum test. K, L γ-H2AX protein level was performed by Western blots. M C57BL/6 mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal administration of ketamine and xylazine and their abdomen were disinfected with ethanol immediately before surgery. A midline laparotomy was performed, and a ligation was performed under the caecum and the other ligation was performed around 3 cm away from the first ligation. BHI, F. nucleatum, Fn.CM and metabolites were injected into the colon loop. After inoculation, the incision was closed. Mice were euthanized 6 h after surgery. The fraction of colon between two ligations were collected for DNA damage assay. N DNA damages were assayed by Western Blot. ***p ≤ 0.001; **p ≤ 0.01; *p < 0.05; NS, not significant. Results of A-L were derived from three independent experiments
