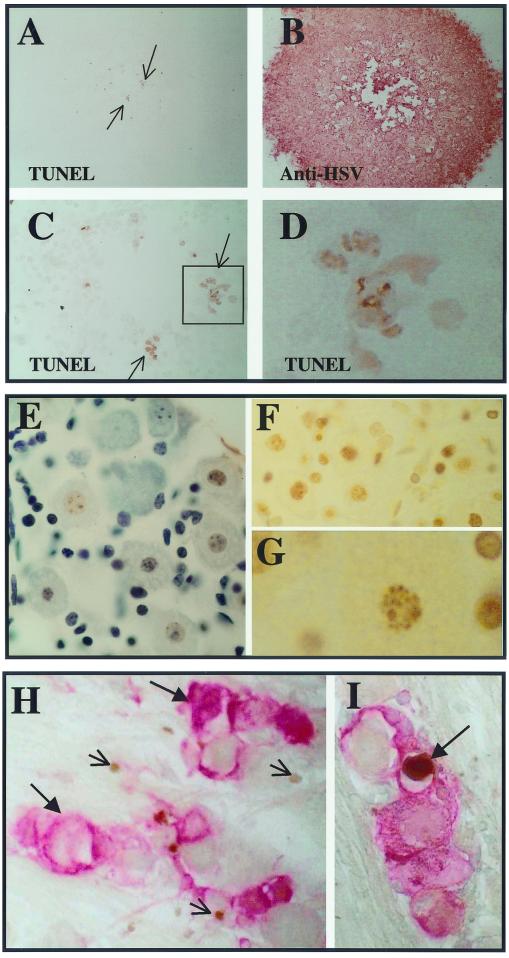
FIG. 6.
(A to D) Results of TUNEL assay on infected RSCs. Panels A and B are at the same magnification. (A) Positive TUNEL staining is indicated by a brown precipitate (arrows) (B) The same plaque was subsequently stained immunohistochemically for HSV proteins (red precipitate). (C) The TUNEL-positive region is enlarged and positive cells are boxed. The boxed region is further enlarged in panel D. (E to G) Micrographs of an uninfected TG that was cultured in the presence of staurosporine to induce apoptosis. The DeadEnd (Promega) colorimetric apoptosis detection system was utilized according to the manufacturer's instructions. (E) A section stained for TUNEL (brown) and subsequently counterstained (blue). Many TUNEL-positive cells, including neurons, are evident. (F) A similar section to that in panel E, prior to counterstaining. Many TUNEL-positive nuclei (brown) are evident. (G) A greater magnification of one of the TUNEL-positive neuronal nuclei of panel F is shown. (H and I) Mice were infected with 17-AH (panel H) or 17-AHRI (panel I) as described in Materials and Methods. Ganglia were processed for TUNEL staining 4 days p.i. The sections were subsequently processed for the immunohistochemical detection of viral proteins as described in Materials and Methods. HSV proteins are stained red (large arrows) and TUNEL staining is brown (small arrows). A positive putative neuron is indicated by an arrow.