Figure 1.
Directed evolution workflows
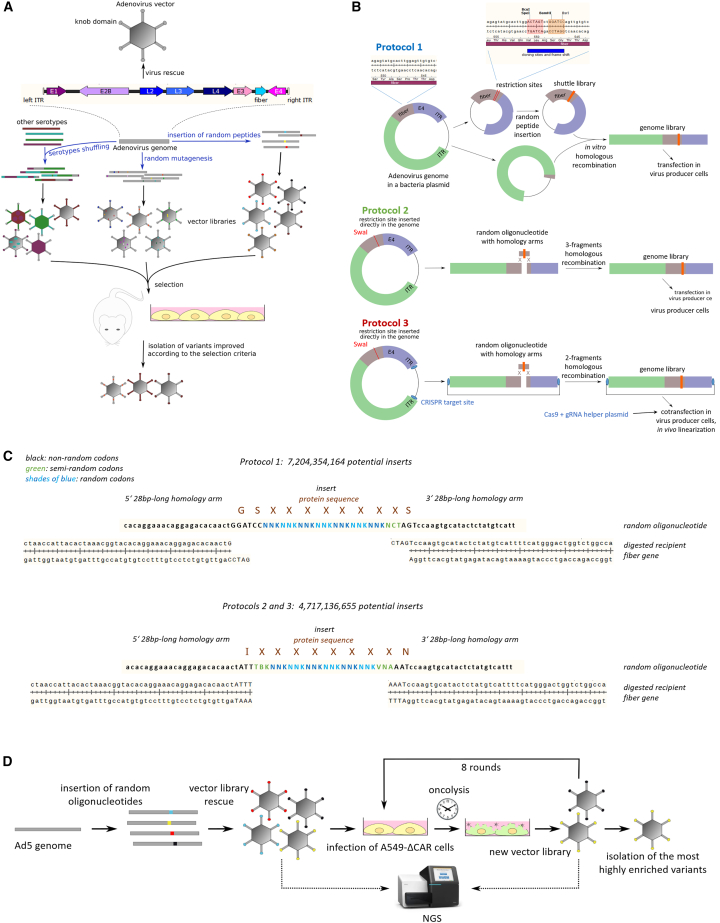
(A) Directed evolution principles. Random libraries can be generated by shuffling of pre-existing viruses, random mutagenesis, or random peptide display. Libraries are subsequently selected in chosen models under stringent conditions to enrich variants optimizing the desired criteria. The schematic of AdV genome represents the ITRs and most major genes at a scale representative of HAdV-C5 WT genome. (B) ADEVO protocols for library generation studied in this article. All protocols are based on the insertion of oligonucleotides containing eight random or semi-random codons in the HI loop of the fiber knob domain. In protocol 1, libraries are first built in a fiber-carrying shuttle plasmid. The shuttle plasmid is then recombined with a truncated AdV genome to reassemble full insert-carrying AdV genomes. In protocol 2, libraries are built in a single step by three-fragment homologous recombination between the left and right parts of the AdV genome and the random oligonucleotide. Protocol 3 involves a single-step, two-fragment homologous recombination, and an in vivo Cas9-mediat`ed AdV genome linearization after transfection. (C) Sequence details of peptide insertions. Random oligonucleotides used for homologous recombination inside the fiber gene HI loop contain 28-nt-long homology arms matching the fiber (lowercase) and restriction sites (uppercase) sequences of the different protocols, and a central insert of 8 random or semi-random codons. (D) Proof-of-concept experiment design. Several libraries were constructed and submitted to eight rounds of selection on A549-ΔCAR cells. Full results are available for one protocol 1 library, two protocol 2 libraries and one protocol 3 library. Library quality was assessed by NGS at different steps of the directed evolution workflow. After selection, the most highly enriched variants were isolated and characterized.