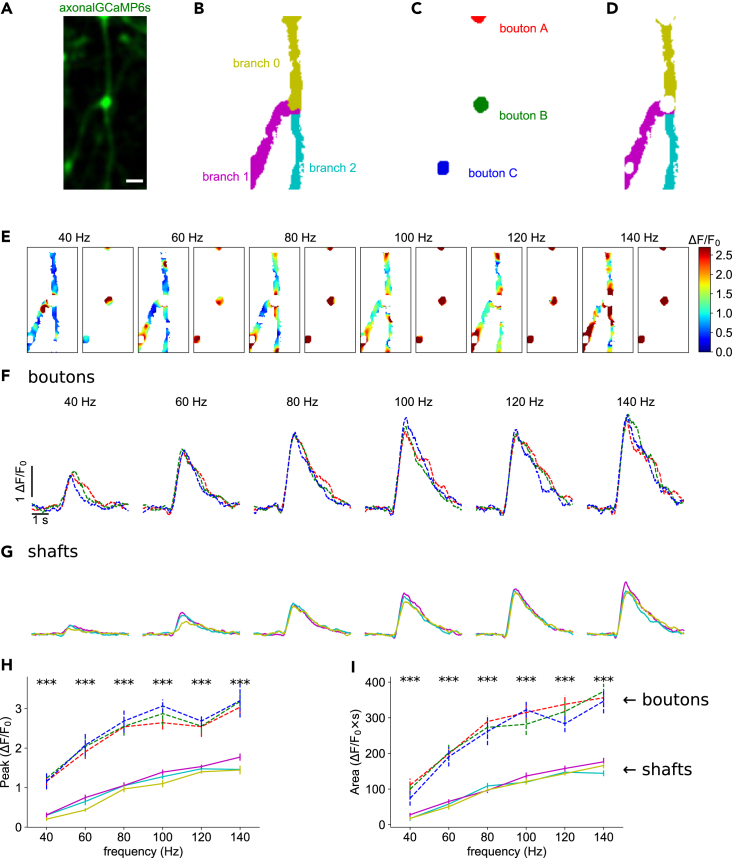
Figure 2.
Increased calcium responses of axonal boutons
(A) Time-averaged image of axon-GCaMP6s activity during electrical stimulation. Scale bar: 2 μm.
(B) Color map of the automatically identified parent (0) and the two secondary axonal branches (1 and 2).
(C) Masks of three axonal boutons (A, B, and C).
(D) Masks of axonal branches after removal of the boutons.
(E) Representative color maps depicting normalized calcium peak amplitudes for axonal branches and boutons at different firing frequencies.
(F) Normalized axon-GCaMP6s/mRuby3 signal for each bouton at different frequencies. Average of 7 trials per frequency. Traces are colored according to the boutons shown in C.
(G) Normalized axon-GCaMP6s/mRuby3 signal for each branch at different frequencies. Average of 7 trials per frequency. Traces are colored according to branches shown in D.
(H) Calcium peak amplitudes of signals from F and G as a function of firing frequency.
(I) Area under the curve of signals from F and G as a function of firing frequency. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Asterisks indicate statistical significance difference between signals; Kruskal-Wallis H-test.