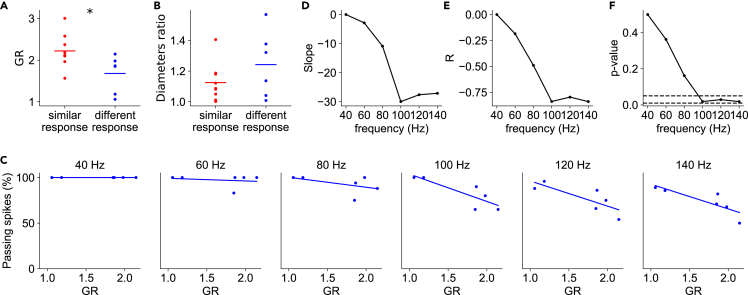
Figure 6.
Spike filtering correlates with axonal branch point geometrical ratio (GR)
(A) GR values of “similar” (n = 9) and “different” (n = 6) response branch points; t test two-sided.
(B) Ratio between diameters of the two secondary branches, “similar” in red and “different” in blue; t test two-sided. The horizontal lines represent the means.
(C) Percentage of propagating spikes as a function of GR for each spike train frequency. Lines represent linear fits to the data.
(D) Slope of the regression line as a function of action potential frequency.
(E) Pearson correlation coefficient (R) between the percentage of passing spikes and GR, as a function of action potential frequency.
(F) p value of the linear regression fitting as a function of the action potential frequency. Dashed lines indicate p values of 0.05 and 0.01.