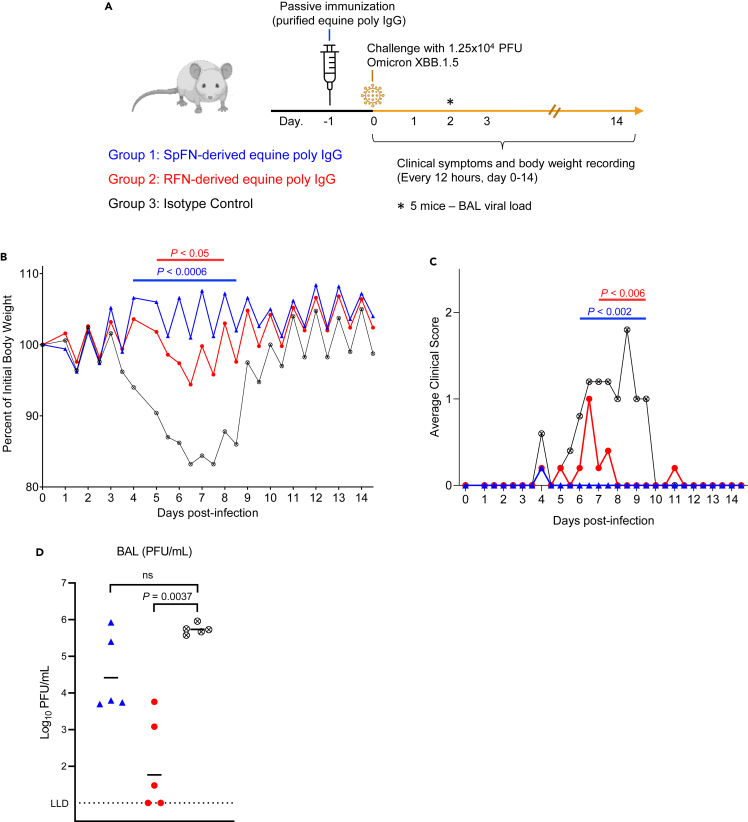
Figure 4.
Passive immunization with purified equine IgG protect mice from SARS-CoV-2 XBB.1.5 challenge
(A) Schematic of K18-hACE2 mice SARS-CoV-2 challenge study. Mice (n = 10/group, 5 female, 5 male) received an intraperitoneal injection of purified IgG from SpFN-immunized horses (blue), or RFN-immunized horses (red), or human IgG1 isotype control mAb (black), one day prior to challenge with 1.25 × 104 PFU of SARS-CoV-2 virus (Omicron XBB.1.5).
(B) Body weight measurements for K18-hACE2 mice over the course of the challenge study (n = 5/group). Percentage of initial weight is plotted. Isotype control mAb (black open X circle), or SpFN-purified IgG (blue triangle) or RFN-purified IgG (red circle). Significant difference for each measurement timepoint between each group compared to the antibody isotype control group, as assessed by t-test is indicated by a horizontal line.
(C) Average cinical score measurements of the K18-hACE2 study groups (n = 5/group). Isotype control mAb (black open X circle), or SpFN-purified IgG (blue triangle) or RFN-purified IgG (red circle). Significant difference for each measurement timepoint between each group compared to the antibody isotype control group, as assessed by t-test is indicated by a horizontal line above the plot.
(D) SARS-CoV-2 viral loads in BAL, were measured 2 days post-challenge in a subset of animals (n = 5/group) by plaque assay. BAL (PFU/mL) viral levels in the two study groups were compared for significance against the control group using a Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA test followed by post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison test.