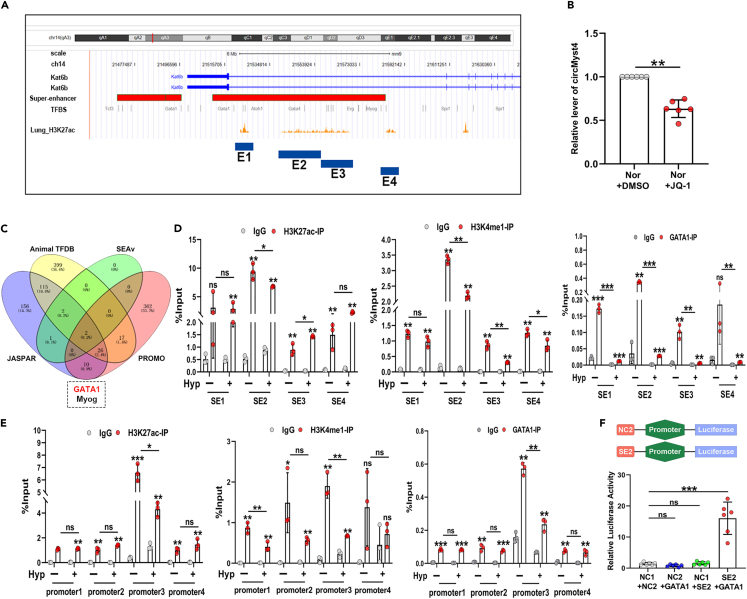
Figure 7.
Superenhancers drive the generation of circMyst4
(A) Gene tracks depicted the superenhancer region of Myst4 in lung tissue with measured H3K27ac marks. According to H3K27ac signal peak, the superenhancer region of Myst4 was divided into four constituents (E1, chr14: 21523088–21524806; E2, chr14: 21546613–21561236; E3, chr14: 21585003–21587120; E4, chr14: 21617293–21618401).
(B) After JQ-1 (a kind of inhibitor of superenhancer) treatment, real-time qPCR analysis of the expression of circMyst4 (n = 6) in PASMCs.
(C) Venn diagram shown that candidate transcription factors bound to the promoter and superenhancer of Myst4.
(D) ChIP-qPCR analysis showed GATA1, H3K27ac and H3K4me1 bound to the second constituent (E2) of superenhancer region of Myst4 (n = 3).
(E) ChIP-qPCR analysis showed GATA1, H3K27ac and H3K4me1 bound to the third segment of promoter region (P3) of Myst4 (n = 3).
(F) The luciferase activities of superenhancer element 2 were measured through dual-luciferase reporter assay in PASMCs (n = 6). Data are shown as means ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni correction and Student’s t test for 2 means. Hyp, hypoxia; Nor, normoxia; ns, not significantly different. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.