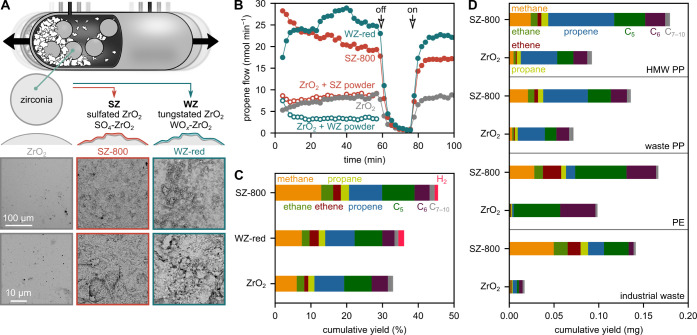
Figure 1.
Mechano-catalytic conversion of plastic (waste) to C1–10 hydrocarbons. (A) Milling container, surface activation strategy, and SEM images of grinding spheres. (B) Propene flow during milling of 2 g model PP with sulfated (SZ-800), tungstated (WZ-red), and untreated (ZrO2) spheres at 30 Hz, compared to milling with untreated spheres and 0.1 g SZ and 0.2 g WZ powder catalysts. The shaking was turned off/on at the indicated points. (C) Cumulative yields during milling of 20 mg model PP for 1 h at 35 Hz with sulfated (SZ-800), tungstated (WZ-red), and untreated (ZrO2) spheres. (D) Cumulative yields during milling of HMW PP (2 g, 30 Hz), waste PP (2 g, 30 Hz), PE (2 g, 35 Hz) and industrial waste (1 g, 30 Hz) for 1 h with sulfated (SZ-800) and untreated (ZrO2) spheres.