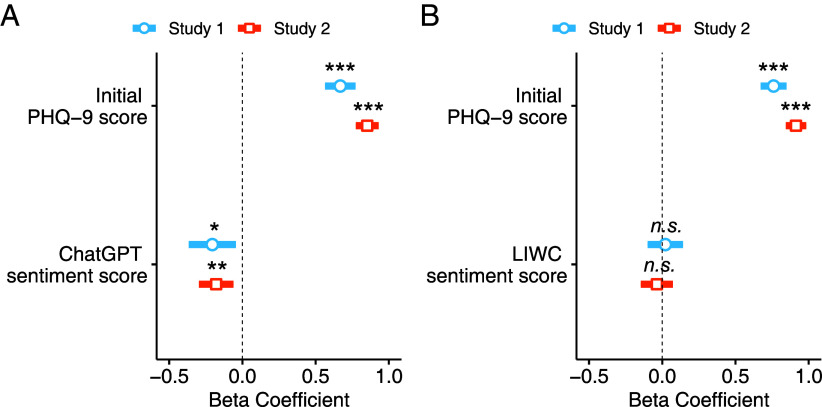
Fig. 2.
Sentiment ratings from LLMs, but not LIWC, predict future depression. (A and B) Robust linear regression predicting future depressive symptom scores (PHQ-9) after three weeks using automatic sentiment ratings by (A) ChatGPT and (B) LIWC. Note that in all models, the PHQ-9 scores at follow-up were used as a dependent variable, and age, gender, and education level were used as covariates. (A) In the analyses using ChatGPT sentiment scores, more negative sentiment scores predicted increased depressive symptoms (i.e., more depressed) at the three-week follow-up in both studies, after controlling for initial depression scores. (B) In analyses using LIWC sentiment scores, more negative sentiment scores did not predict increased depressive symptoms at the three-week follow-up in both studies, after controlling for initial depression scores. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.