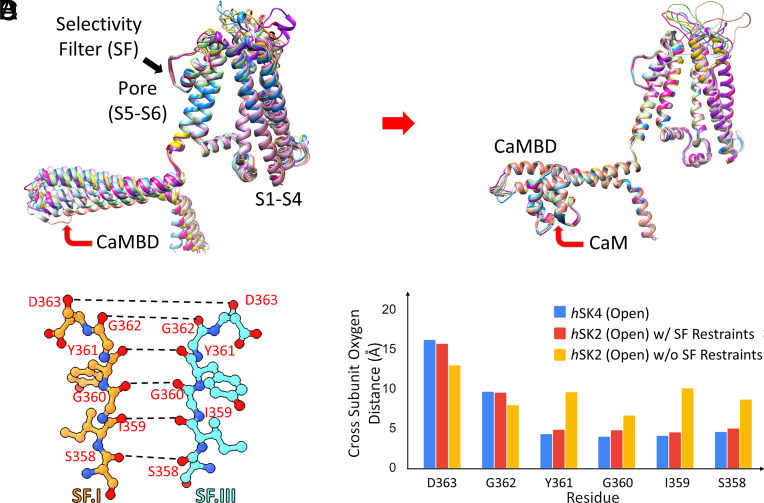
Fig. 2.
Homology models of hSK2–CaM complexes based on the open state of hSK4-CaM cryo-EM structure (PDB: 6CNO) using Rosetta structural modeling. (A) Top 10 homology models of the hSK2 channel without CaM show large movements in the CaMBD in the C terminus of hSK2 channels, due to the flexible loop connecting pore-lining transmembrane helix S6 to the CaMBD. (B) Inclusion of CaM in homology modeling shows convergence among the top 10 models for the CaMBD. (C) Selectivity filter (SF) of the hSK2 channel shown using ball-and-stick representation with the distances of backbone carbonyl oxygen atoms (red balls) shown as dashed black lines (amino acid residue numbering based on the hSK2 channel). Nitrogen atoms are shown as blue balls. (D) Cross-subunit backbone carbonyl oxygen distances for SF amino acid residues of the open state of hSK4 cryo-EM structure (blue bars), hSK2–CaM homology models with 100 kcal/mol/Å2 restraints being applied to the backbone Cα atoms (red bars), and hSK2–CaM homology models without (w/o) restraints (yellow bars).