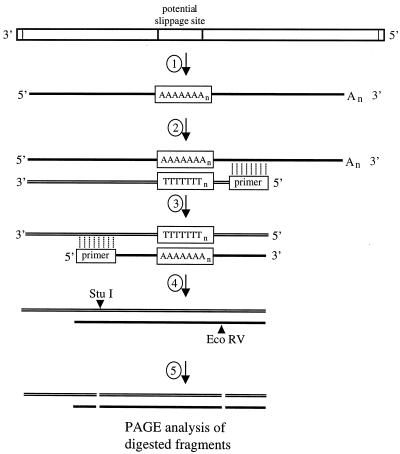
FIG. 4.
Schematic representation of the RT/Klenow slippage assay used to analyze RNAs for evidence of slippage by the VSV polymerase. 1, VSV genomes or subgenomic templates that included a potential slippage sequence (boxed) were used as templates for VSV polymerase-directed RNA synthesis. The slippage sequence comprised a U7 tract preceded by a tetranucleotide sequence which was the site of all specific template alterations. 2, first-strand cDNA synthesis by reverse transcriptase in the presence of [35S]dATP was primed using an oligonucleotide that annealed downstream of the slippage sequence. 3, labeled cDNAs acted as templates for unlabeled second-strand synthesis, using the Klenow fragment of E. coli DNA polymerase I to extend an oligonucleotide primer that annealed to a site corresponding to the upstream side of the slippage site. 4, resulting cDNAs were digested with restriction enzymes EcoRV and StuI. 5, digested cDNAs were denatured and subjected to PAGE and autoradiography to visualize the labeled cDNA fragments.