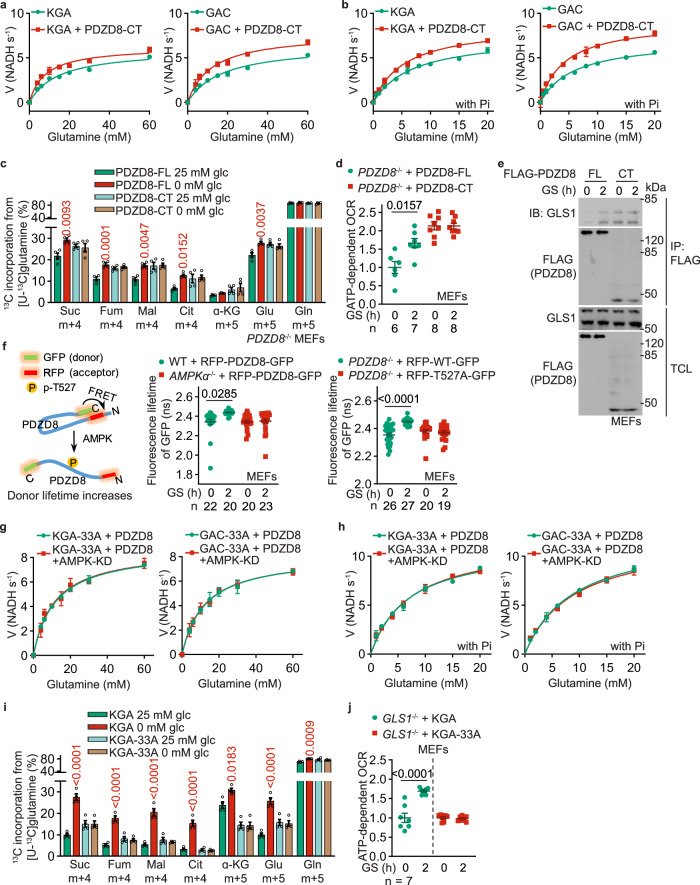
Fig. 4. Interaction of PDZD8 promotes GLS1 activity.
a, b PDZD8-CT that constitutively interacts with GLS1, promotes GLS1 activity in vitro independently of AMPK. Recombinant KGA (left panel) or GAC (right panel) isozyme of GLS1 was mixed with recombinant PDZD8-CT, followed by determining the enzymatic activities of GLS1 in the presence (b) or absence (a) of 20 mM K2HPO4 (Pi). Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 3 for each condition. See also Km and kcat values for each reaction in Supplementary information, Table S2. The experiments in (a) and Fig. 3c were performed at the same time and shared control (the KGA- and GAC-alone groups), and ditto for b and Fig. 3f. c, d PDZD8-CT promotes glutaminolysis and OCR in high glucose. PDZD8–/– MEFs were infected with lentiviruses carrying full-length (FL) PDZD8 or PDZD8-CT, followed by incubating in a medium containing doxycycline for 12 h. Cells were then labeled with [U-13C]-glutamine to determine glutaminolysis (c, performed as in Fig. 1a) or subjected to Seahorse analyzer to determine OCR (d). Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n = 4 (c), or labeled on the panel (d; representing biological replicates) for each condition; P values were determined by two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey (P values in c represent the comparisons between the starved and the unstarved groups of each genotype). e AMPK releases the autoinhibition of PDZD8-NT towards PDZD8-CT. MEFs stably expressing FLAG-tagged PDZD8-FL or PDZD8-CT were glucose-starved for 2 h, followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG and immunoblotting for co-precipitated GLS1. f AMPK causes PDZD8-NT to move away from PDZD8-CT. AMPKα–/– MEFs (middle panel), or PDZD8–/– MEFs (right panel) were infected with lentiviruses carrying RFP-PDZD8-GFP (middle and right panels) or RFP-PDZD8-T527A-GFP (right panel), followed by determination of the fluorescence lifetime of GFP (FRET donor; see principles of this assay on the left panel). Data are shown as mean ± SEM; n values were labeled on the panel representing cell numbers; P values were determined by two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey. g–j GLS1-33A that loses the interface for PDZD8 fails to promote GLS1 activity (g, h), glutaminolysis (i), or OCR (j) in low glucose. Experiments in g and h were performed as in a and b, except that the recombinant KGA-33A (left panel) and GAC-33A (right panel) were mixed with AMPK-phosphorylated PDZD8. See also lowered Km and increased kcat values in each reaction in Supplementary information, Table S2. Experiments in i and j were performed as in c and d, except that GLS1–/– MEFs with WT KGA or KGA-33A stably expressed were used. Data are mean ± SD; n = 3 (g, h) or 4 (i), or labeled on the panel (j; representing biological replicates) for each condition; P values were determined by two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey (i) or by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (j). Experiments in this figure were performed three times.