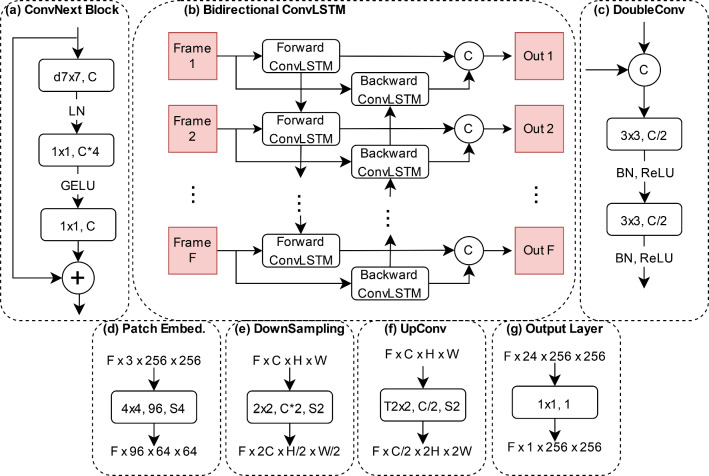
Fig. 2.
Key components of our network. The information in the boxes refers to kernel size, output channel size and stride. If no stride is given, it is set to 1. The C in a circle stands for concatenation along the channel dimension. a ConvNextBlock—the main encoder building block. The ‘d’ in front of the kernel size stands for depthwise convolution. b Bidirectional ConvLSTM—fuses information across frames. c DoubleConv module—merges skip connection data with upsampled information during the decoding process. d Patch embedding layer—serves as the first encoder layer. e Downsampling layer—used to reduce the spatial dimension and increase the channel dimension during encoding. f Upsampling layer—used to increase the spatial dimensions and decrease the channel dimension during decoding. The ‘T’ in front of the kernel size refers to transposed convolution. g Output layer—serves as the final model layer and reduces the channel dimension to 1