Abstract
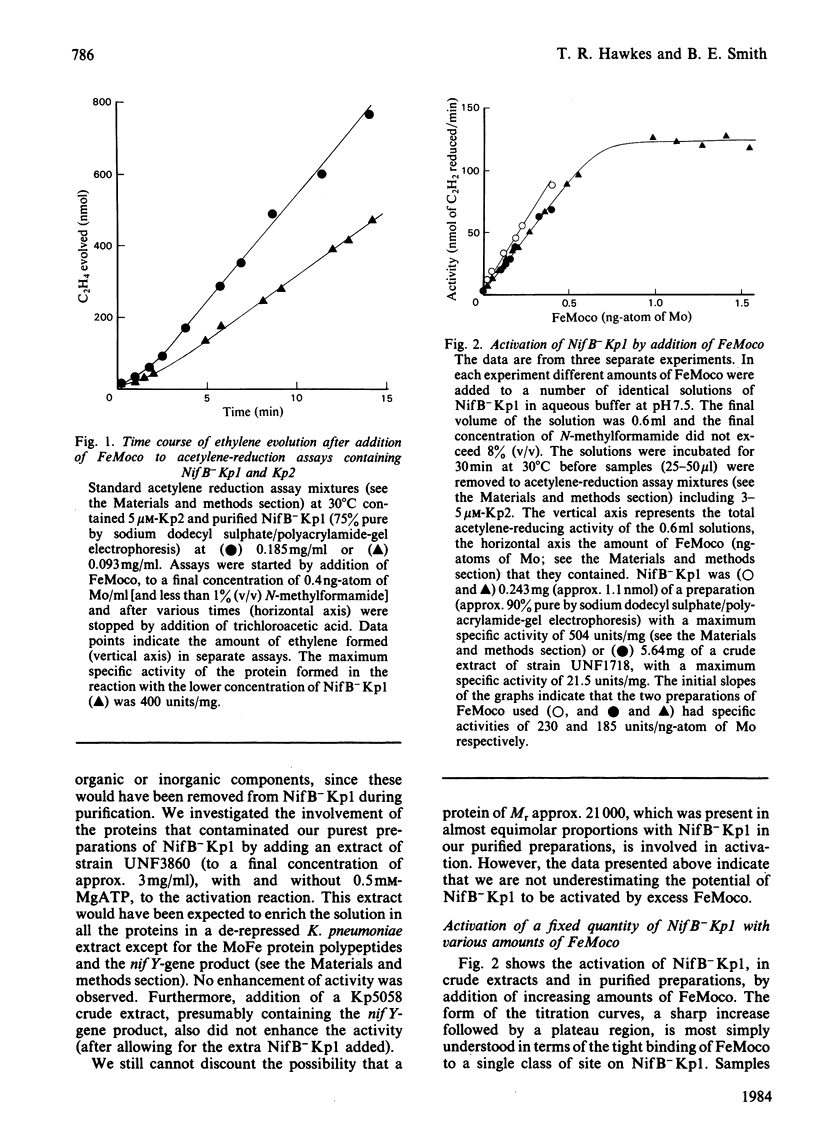
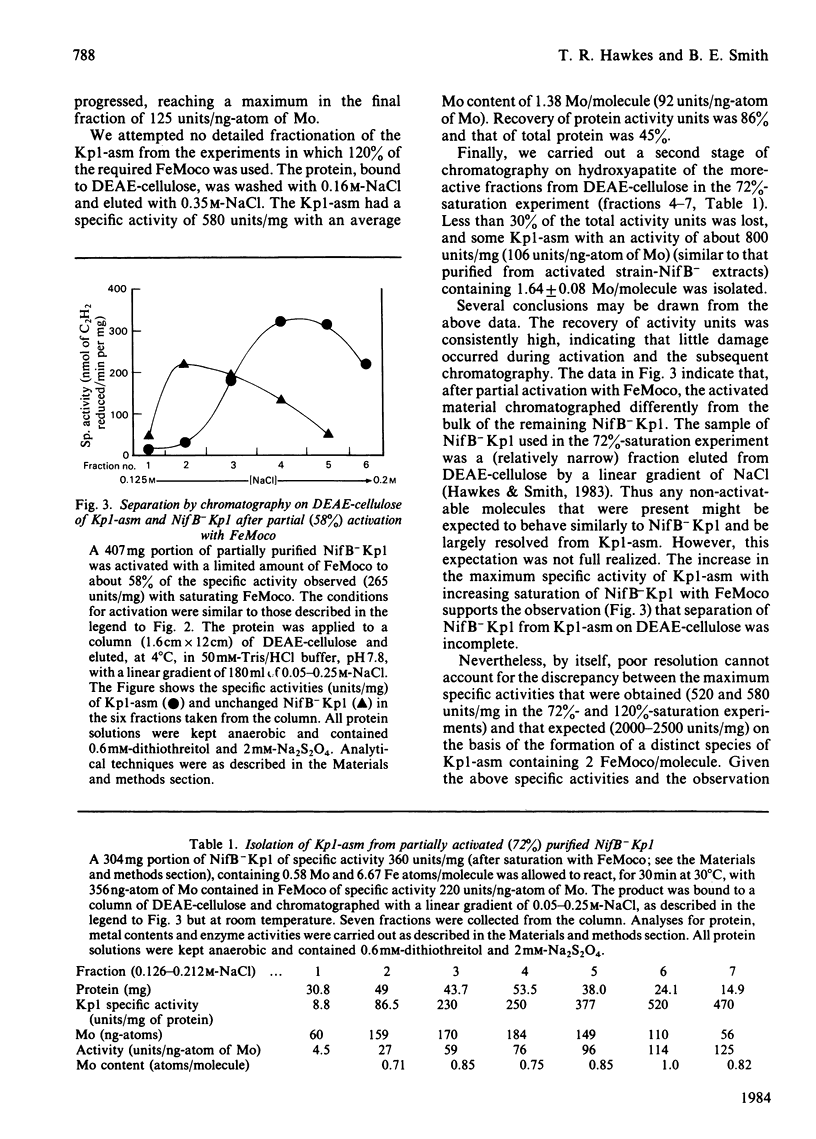
The inactive MoFe protein (NifB-Kp1) of nitrogenase from nifB mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae may be activated by addition of the iron-molybdenum cofactor (FeMoco) extracted from active MoFe protein (Kp1). However, when apparently saturated with FeMoco, our preparations of NifB-Kp1 yielded activated protein, Kp1-asm, with a specific activity that was at best only 40% of that expected. This was not due to degradation of Kp1-asm, NifB-Kp1 or FeMoco during the activation reaction. Nor could activation be enhanced by addition of other nif-gene products or other proteins. Whereas fully active Kp1 contains 2 FeMoco/molecule, apparent saturation of our NifB-Kp1 preparations required the binding of only 0.4-0.65 FeMoco/molecule. By using chromatography Kp1-asm could be largely resolved from NifB-Kp1 that had not been activated. However, we were unable to isolate fully active MoFe protein (i.e. Kp1-asm containing 2 FeMoco/molecule) from solutions of NifB-Kp1 activated with FeMoco. The maximum activity/ng-atom of total Mo obtained for our purified Kp1-asm was approximately half the maximum activity for FeMoco. Since all NifB-Kp1 preparations contained some Mo, we suggest that FeMoco activated only those NifB-Kp1 molecules already containing one atom of (non-FeMoco) Mo, thus forming Kp1-asm with 2 Mo but only 1 FeMoco/molecule. Kp1-asm was identical with normal Kp1 in terms of its Mr, stability, e.p.r. signals, pattern of substrate reductions, CO inhibition and ATP/2e ratio. In addition, for preparations of differing specific activity, there was a constant and identical relationship between the e.p.r. signal intensity (from FeMoco) and the activity of both Kp1 and Kp1-asm. Assuming the above hypothesis on the structure of Kp1-asm, these data demonstrate that the two FeMoco sites in wild-type Kp1 operate independently.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess B. K., Jacobs D. B., Stiefel E. I. Large-scale purification of high activity Azotobacter vinelandII nitrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 10;614(1):196–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Smith B. E., Cook K. A., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):655–675. doi: 10.1042/bj1280655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T. R., Lowe D. J., Smith B. E. Nitrogenase from Klebsiella pneumoniae. An e.p.r. signal observed during enzyme turnover under ethylene is associated with the iron-molybdenum cofactor. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):495–497. doi: 10.1042/bj2110495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T. R., McLean P. A., Smith B. E. Nitrogenase from nifV mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae contains an altered form of the iron-molybdenum cofactor. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):317–321. doi: 10.1042/bj2170317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T. R., Smith B. E. Purification and characterization of the inactive MoFe protein (NifB-Kp1) of the nitrogenase from nifB mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):43–50. doi: 10.1042/bj2090043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh B. H., Henzl M. T., Christner J. A., Zimmermann R., Orme-Johnson W. H., Münck E. Nitrogenase XII. Mössbauer studies of the MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 29;623(1):124–138. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam S., Eady R. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae: reductant-independent ATP hydrolysis and the effect of pH on the efficiency of coupling of ATP hydrolysis to substrate reduction. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 28;110(1):35–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimber S. J., Bishop E. O., Smith B. E. Evidence on the role(s) of ATP in the mechanism of nitrogenase, from proton NMR relaxation studies on metal and nucleotide binding to the molybdenum-iron protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 10;705(3):385–389. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. J., Lynden-Bell R. M., Bray R. C. Spin-spin interaction between molybdenum and one of the iron-sulphur systems of xanthine oxidase and its relevance to the enzymic mechanism. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):239–249. doi: 10.1042/bj1300239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean P. A., Dixon R. A. Requirement of nifV gene for production of wild-type nitrogenase enzyme in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):655–656. doi: 10.1038/292655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M., Filser M., Dixon R., Elmerich C., Sibold L., Houmard J. The use of translocatable genetic elements to construct a fine-structure map of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogen fixation (nif) gene cluster. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Apr;117(2):509–520. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-2-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortenson L. E., Thorneley R. N. Structure and function of nitrogenase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:387–418. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Levy M. A., Orme-Johnson W. H. Metal and sulfur composition of iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):147–150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings J., Shah V. K., Chisnell J. R., Brill W. J., Zimmermann R., Münck E., Orme-Johnson W. H. Novel metal cluster in the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. Spectroscopic evidence. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1001–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Brill W. J. Regulation and characterization of protein products coded by the nif (nitrogen fixation) genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):267–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.267-279.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. E., Richards A. J., Thomson A. J., Hawkes T. R., Smith B. E. Low-temperature magnetic-circular-dichroism spectroscopy of the iron-molybdenum cofactor and the complementary cofactor-less MoFe protein of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 15;219(2):495–503. doi: 10.1042/bj2190495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Isolation of a molybdenum--iron cluster from nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3438–3440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Isolation of an iron-molybdenum cofactor from nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Lang G. Mössbauer spectroscopy of the nitrogenase proteins from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Structural assignments and mechanistic conclusions. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):169–180. doi: 10.1042/bj1370169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Lowe D. J., Bray R. C. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae: electron-paramagnetic-resonance studies on the catalytic mechanism. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):641–643. doi: 10.1042/bj1300641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Lowe D. J., Bray R. C. Studies by electron paramagnetic resonance on the catalytic mechanism of nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;135(2):331–341. doi: 10.1042/bj1350331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Lowe D. J., Chen G. X., O'Donnell M. J., Hawkes T. R. Evidence on intramolecular electron transfer in the MoFe protein of nitrogenase from Klebsiella pneumoniae from rapid-freeze electron-paramagnetic-resonance studies of its oxidation by ferricyanide. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):207–213. doi: 10.1042/bj2090207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., O'Donnell M. J., Lang G., Spartalian K. A Mössbauer spectroscopic investigation of the redox behaviour of the molybdenum-iron protein from Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase. Mechanistic and structural implications. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):449–455. doi: 10.1042/bj1910449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G. Isolation of thiomolybdate compounds from the molybdenum-iron protein of clostridial nitrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 15;91(2):345–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


