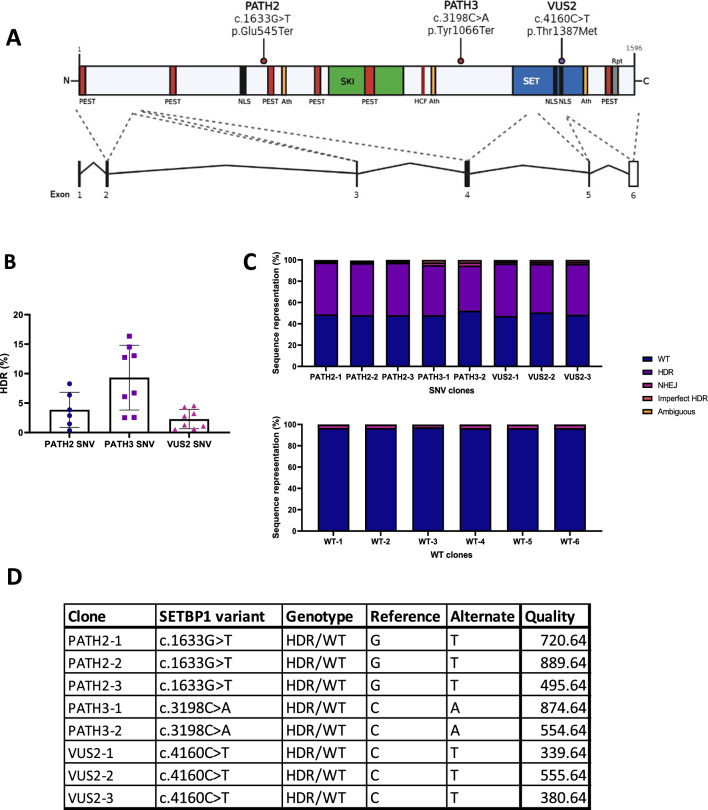
Fig. 1.
Generation of iPSC clones harbouring SETBP1 variants using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing. A Schematic representation of the SETBP1 protein indicating the PATH2, PATH3 and VUS2 variants introduced into the KOLF2 iPSC genome using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing. Five exons encode isoform A (1596 amino acid residues) of the SETBP1 protein. Truncating variants PATH2 and PATH3 are not located in any functional domains, however the missense variant, VUS2, is in an NLS region within the SET-binding domain. PEST: proline, glutamic acid, serine, and threonine rich sequence; NLS: nuclear localisation signal; Ath: AT hook; SKI: SKI homology region; HCF: HCF-1 binding motif; SET: SET-binding domain; Rpt: repeat. B CRISPR/Cas9 HDR efficiency for SETBP1 SNV integration into iPSC genomes. Data presented as mean ± s.d. HDR: homology directed repair; SNV: single nucleotide variant. C SETBP1 SNV and WT derived cell clones. Bar graphs show genotype for three heterozygous PATH2 variant cell lines, two heterozygous PATH3 variant cell lines, three heterozygous VUS2 variant cell lines, and the six wild-type clones selected as isogenic controls. SNV: single nucleotide variant; WT: wild-type; NHEJ: non-homologous end-joining. D Table of variant calling metrics for SETBP1 in NPC samples. Quality: Phred-scaled quality score