Fig. 6 |. Vascular, perivascular and lymphatic cells in the human breast.
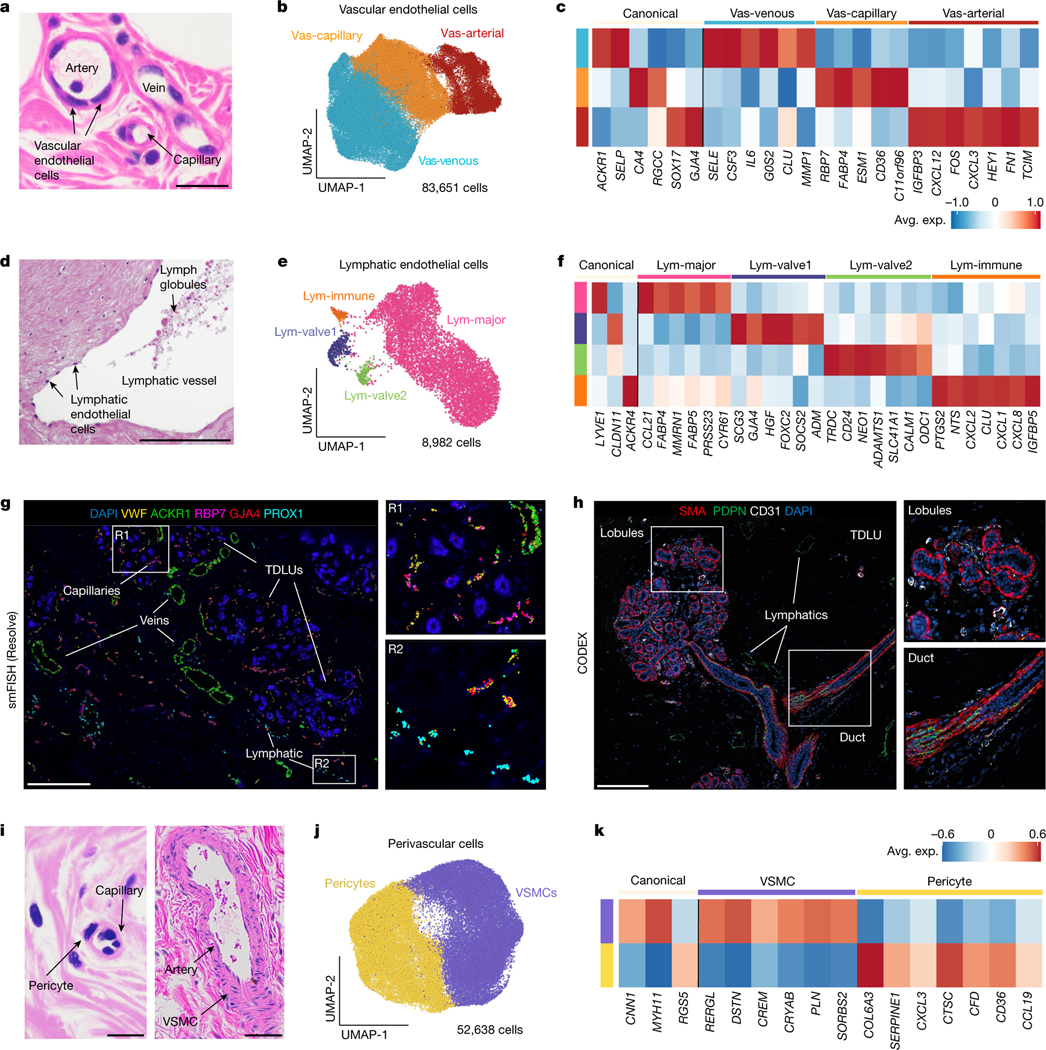
a, Histopathological section showing an artery, vein and capillary structure in normal breast tissue. b, UMAP representation of 83,651 vascular endothelial cells showing 3 major cell states. c, Canonical and top genes expressed for each vascular endothelial cell state, using averaged values from the scRNA-seq data. d, Histopathological section showing a lymphatic duct in the breast tissue. e, UMAP representation of 8,982 lymphatic endothelial cells, showing 4 major cell states. f, Expression of canonical and top genes for each lymphatic cell state, averaged from the scRNA-seq data. g, smFISH (Resolve) data from patient P47 (P47-S1) showing a subset of vascular gene markers (VWF, ACKR1, RBP7 and GJA4) and lymphatic markers (PROX1), with two enlarged regions (R1 and R2). h, CODEX data from patient P130 showing a TDLU region with vascular cells (anti-CD31) and lymphatic cells (anti-PDPN) cells, and basal cells labelled (anti-SMA) with two enlarged regions. i, Histopathological sections showing a pericyte and capillary structure, as well as an artery and VSMCs in normal breast tissue. j, UMAP projection and clustering of 52,638 perivascular cells, showing 2 cell states. k, Canonical markers and the top genes expressed for each perivascular cell state from averaged scRNA-seq data. Scale bars, 50 μm (a, d and i) and 500 μm (g and h).
