Abstract
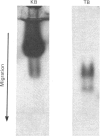
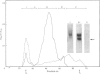
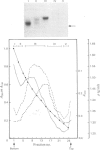
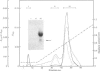
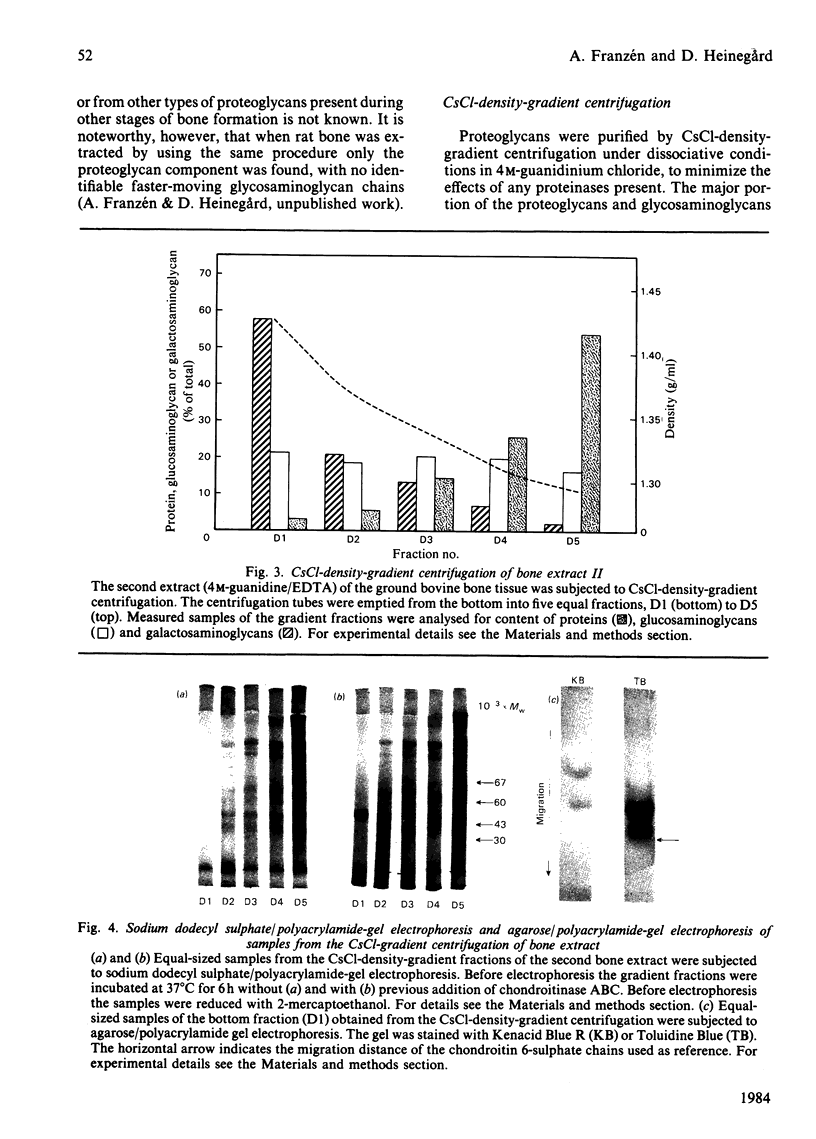
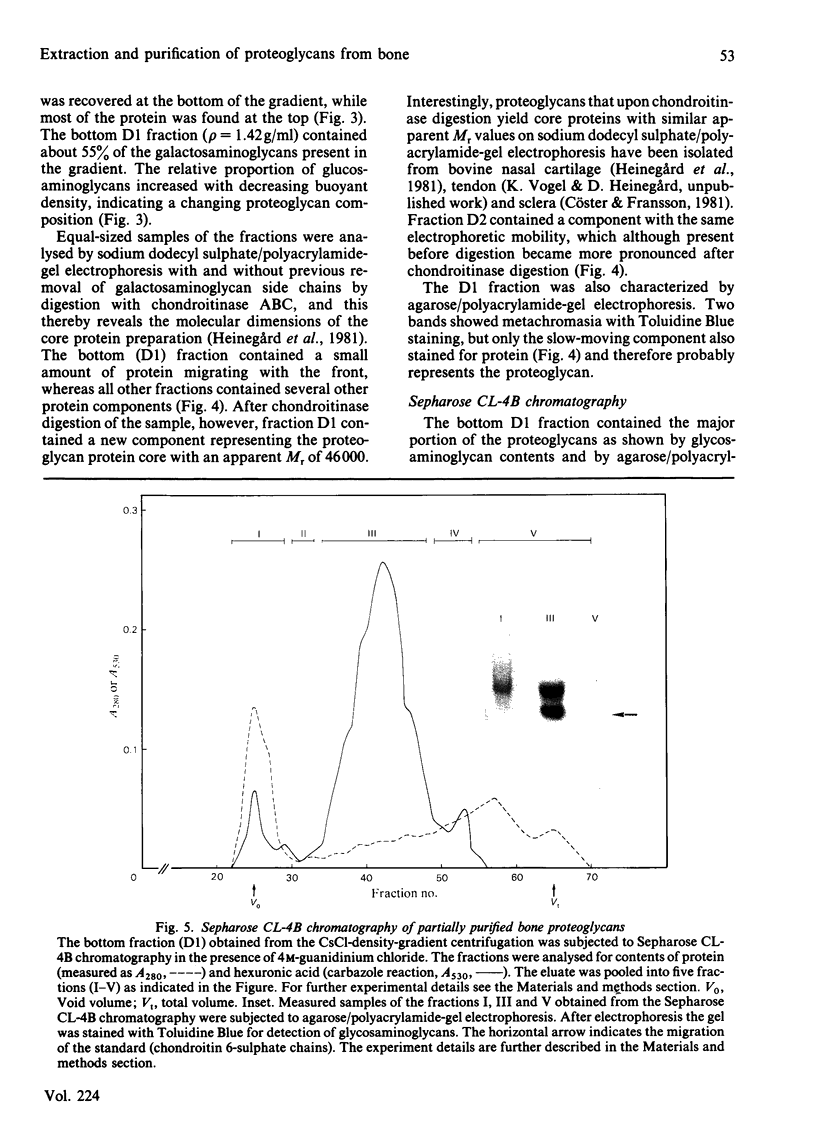
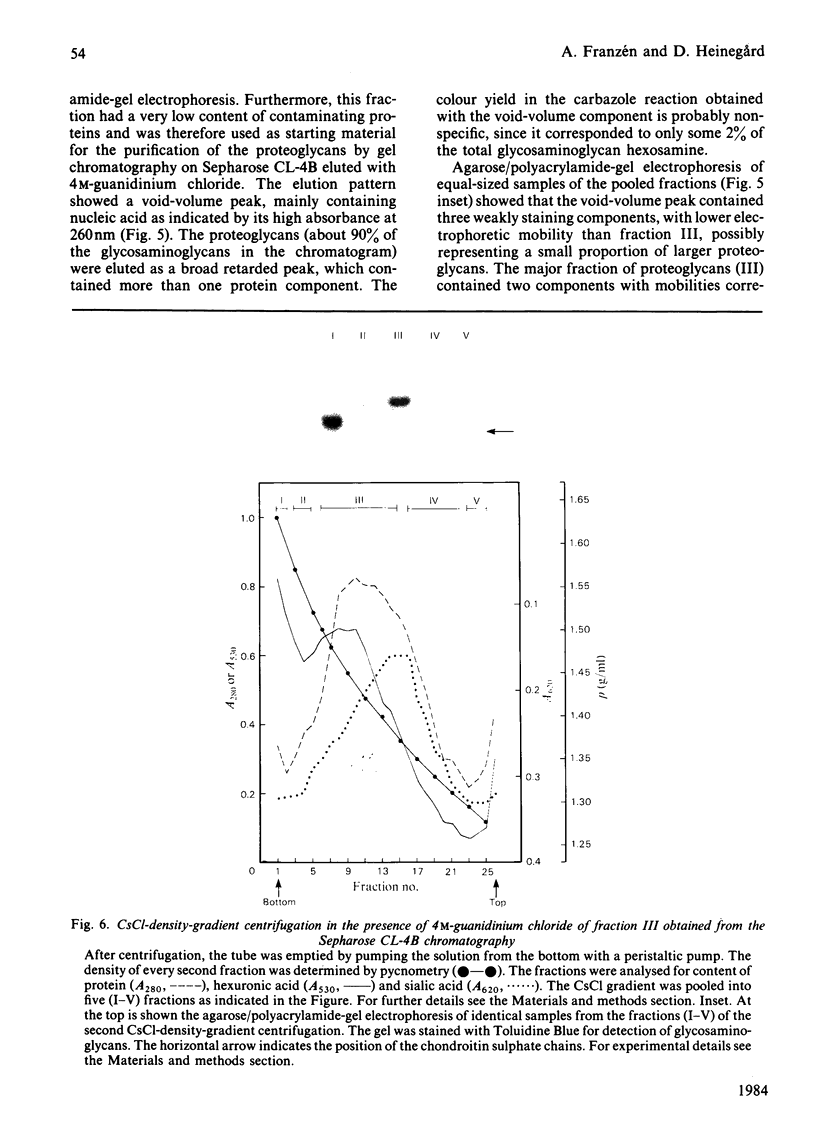
Proteoglycans were extracted in good yields from the mineralized matrix of ground bovine bone, by using a two-step extraction procedure. Proteoglycans (8% of total), not associated with the bone mineral, were extracted at - 20 degrees C with 4M-guanidinium chloride containing proteinase inhibitors. Proteoglycans associated with the mineral, which accounted for 60% of the total, were then solubilized when EDTA was added to the extraction solvent. They were fractionated and purified in the presence of 4M-guanidinium chloride by CsCl-density-gradient centrifugations followed by chromatography on Sepharose CL-4B. Further purification was obtained by chromatography on DEAE-cellulose and hydroxyapatite in the presence of 7 M-urea. Three populations of proteoglycans and additional glycosaminoglycan peptides were obtained. The molecular dimensions of both intact molecules and of their side chains as well as their amino acid composition were different, indicating that they represent separate molecular entities. The main proteoglycan self-aggregated in the absence of 4M-guanidinium chloride or 7 M-urea, a property that was abolished when the proteoglycan core protein was fragmented.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews A. T., Herring G. M., Kent P. W. Some studies on the composition of bovine cortical-bone sialoprotein. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):705–715. doi: 10.1042/bj1040705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson I., Heinegård D. Fractionation of proteoglycans from bovine corneal stroma. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):491–500. doi: 10.1042/bj1450491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson D. M. Structures and immunochemical properties of oligosaccharides isolated from pig submaxillary mucins. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):616–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cöster L., Fransson L. A. Isolation and characterization of dermatan sulphate proteoglycans from bovine sclera. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):143–153. doi: 10.1042/bj1930143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engfeldt B., Hjerpe A. Glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans of human bone tissue at different stages of mineralization. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1976 Jan;84(1):95–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. W., Termine J. D., Dejter S. W., Jr, Whitson S. W., Yanagishita M., Kimura J. H., Hascall V. C., Kleinman H. K., Hassell J. R., Nilsson B. Proteoglycans of developing bone. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6588–6594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Paulsson M., Inerot S., Carlström C. A novel low-molecular weight chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan isolated from cartilage. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):355–366. doi: 10.1042/bj1970355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring G. M. Studies on the protein-bound chondroitin sulphate of bovine cortical bone. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(1):41–49. doi: 10.1042/bj1070041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjertquist S. O., Vejlens L. The glycosaminoglycans of dog compact bone and epiphyseal cartilage in the normal state and in experimental hyperparathyroidism. Calcif Tissue Res. 1968 Dec 18;2(4):314–333. doi: 10.1007/BF02279220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jourdian G. W., Dean L., Roseman S. The sialic acids. XI. A periodate-resorcinol method for the quantitative estimation of free sialic acids and their glycosides. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 25;246(2):430–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander L. S., De Luca S., Nilsson B., Hascall V. C., Caputo C. B., Kimura J. H., Heinegard D. Oligosaccharides on proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6084–6091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt C. A., Muir H. Gel electrophoresis of proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans on large-pore composite polyacrylamide-agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1971 Dec;44(2):612–622. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6151–6159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Sommarin Y., Heinegård D. Metabolism of cartilage proteins in cultured tissue sections. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):659–667. doi: 10.1042/bj2120659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddi A. H., Hascall V. C., Hascall G. K. Changes in proteoglycan types during matrix-induced cartilage and bone development. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2429–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth A., Veis A. The isolation of anionic phosphoproteins from bovine cortical bone via the periodate solubilization of bone collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):414–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]