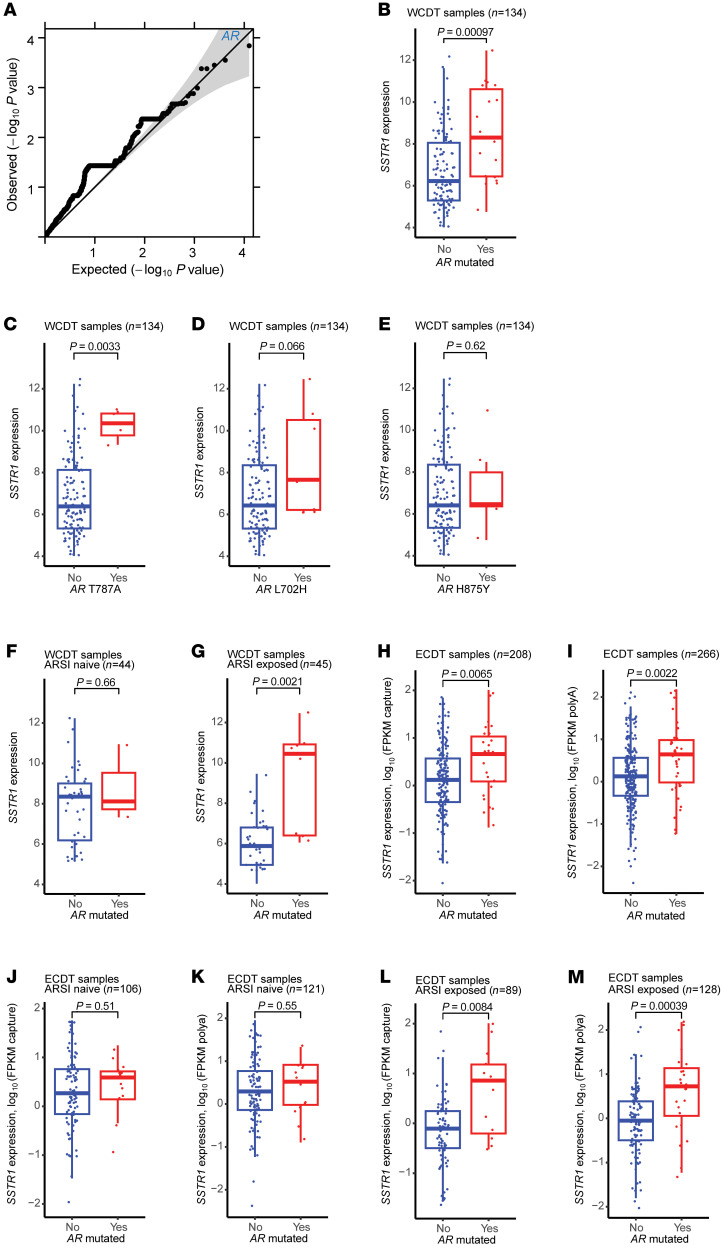
Figure 6. AR mutations are associated with higher SSTR1 mRNA in ARSI-exposed mCRPC.
(A) Quantile-quantile plot of P values (t test as implemented in the linear regression model) shows AR to be the gene most significantly associated with SSTR1 mRNA expression. (B) AR-mutated mCRPC had higher SSTR1 expression in the WCDT. (C–E) Single-mutation analysis in WCDT samples demonstrated T878A to be the main contributor to the gene-level association, with L702H and H875Y showing trends in the same direction. (F and G) AR-mutated status predicted higher SSTR1 expression only in ARSI-exposed tumors in the WCDT dataset. (H and I) The positive association between AR mutation status and SSTR1 mRNA was replicated in the ECDT dataset, where analyses were stratified by the RNA-Seq method (capture vs. polyA). (J–M) Similarly, in the ECDT dataset, AR-mutated status predicted higher SSTR1 expression in ARSI-exposed, but not ARSI-naive, mCRPC. All P values were calculated using the Wilcoxon test for B–M.