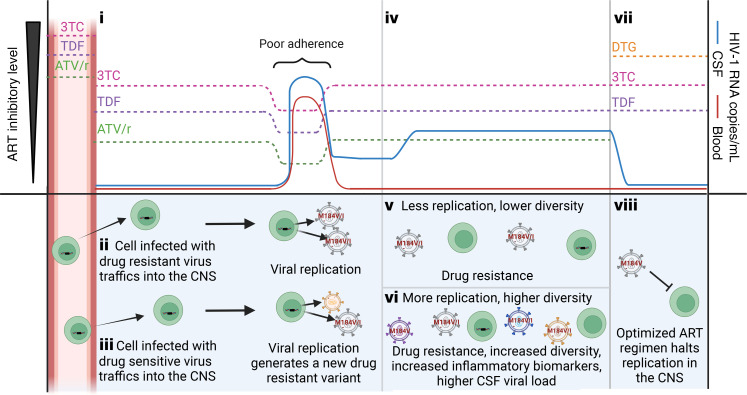
Figure 6. Model of the emergence of NSE during treatment with an ART regimen representative of those used in this cohort.
(i) Most drugs are at lower concentrations in the CSF (86). Despite the overall low levels of protein in the CSF, most ATV in the CSF is protein bound (54), thus reducing the amount of available ATV (54) to noninhibitory levels (86). In contrast, TDF and 3TC are primarily unbound in the CSF. In this drug regimen (TDF/3TC/ATV/r, the most common regimen in our cohort), 3TC is likely the only drug at inhibitory levels in CSF. During a period of poor adherence, the concentration of drug falls and the CSF HIV-1 RNA rises. Upon returning to adherence, drug levels rise and HIV-1 RNA decreases. Return to adherence will select for the M184V mutation (conveying resistance to 3TC). (ii) Resistant virus can reach the CNS as a migrating CD4+ T cell carrying a provirus with the M184V mutation or (iii) evolve in the CNS during replication when all 3 drugs are at noninhibitory levels. (iv) HIV-1 RNA in the CSF remains detectable and may increase as the drug-resistant virus replicates. (v and vi) Replication increases genetic diversity, CSF HIV-1 RNA, and inflammatory biomarkers. Both v and vi are associated with the spread of drug resistant virus and an elevation in CSF WBC. (vii) Optimization of ART to a regimen with good CNS penetration and to which the NSE virus is sensitive will (viii) stop replication and improve symptoms. Created with BioRender.