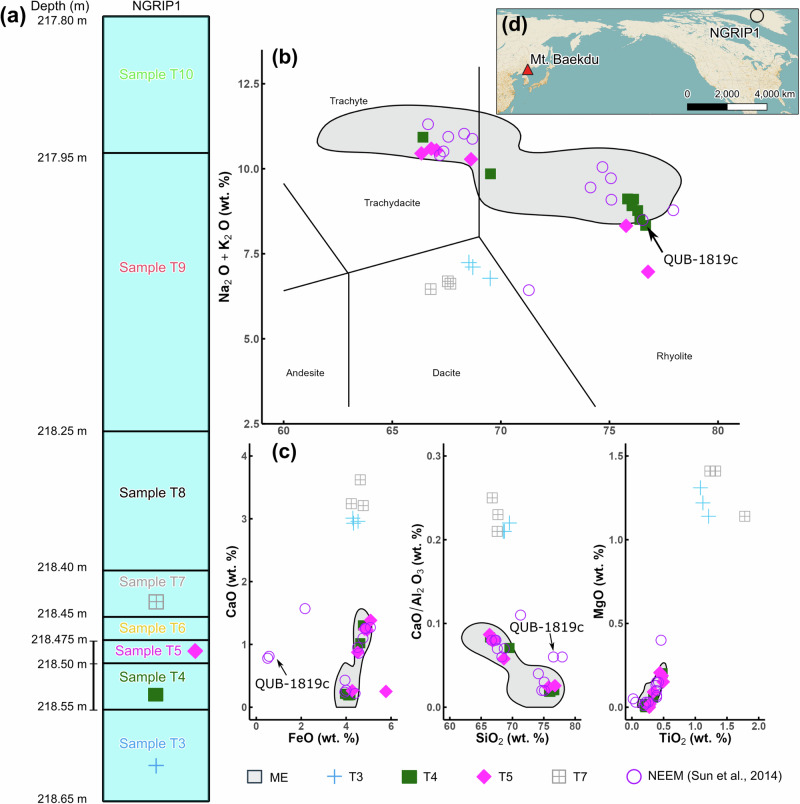
Fig. 1. Stratigraphy and geochemistry of shards found in NGRIP1 and NEEM-2011-S16 cores.
QUB-1819c is a shard potentially corresponding to a Japanese volcano (see Supplementary Note 1) (QUB stands for Queen’s University Belfast). a Schematic diagram of the NGRIP1 ice core. b Total alkali versus silica (TAS) diagram60. c Additional major oxide bi-plots for glass shards. Only samples for which analytical totals exceeded 90 % and those that might represent a tephra population are shown. Shards in sample T7 were measured by scanning electron microscope energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS); all other shards were measured by wavelength dispersive spectroscopy (WDS). Gray shading characterizes the previously reported range of ME glass geochemistry for both proximal and distal deposits6,9,61,62. Tephra populations in T3 and T7 may correspond to fallout from Mt. Rainier eruptions (Supplementary Note 1). d Location of Mt. Baekdu and NGRIP1 core.