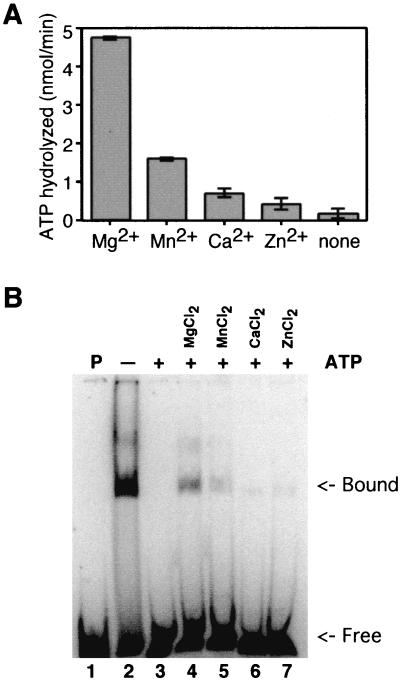
FIG. 3.
Effects of divalent cations. (A) ATPase. Each reaction mixture contained a 6 mM concentration of the indicated divalent cation salt. ATPase reaction mixtures contained 2 mM ATP, 0.1 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP, a 6 mM concentration of the indicated divalent cation chloride salt, 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 0.1 mM EDTA, 15 mM NaCl, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 140 fmol of P143, and 0.25 μg of activated calf thymus DNA in a final volume of 20 μl. Samples were incubated at 30°C for 30 min and were then terminated by the addition of 25 mM EDTA. Polyethyleneimine thin-layer plates were spotted with 1 μl of each reaction, and the hydrolyzed, radiolabeled phosphate was separated from the input triphosphate by development in 1 M formic acid and 0.5 M LiCl. Thin-layer chromatography plates were dried and exposed to PhosphorImager screens. Results were quantitated using a Storm PhosphorImager. Background levels of hydrolysis in the absence of enzyme were subtracted. An assay was performed in triplicate, and standard error is indicated. (B) DNA binding. Lane 1 contains probe without enzyme. Lanes 2 to 7 contain P143 in a fivefold-molar excess over the 88-nucleotide radiolabeled probe. Lanes 3 to 7 contain 2 mM ATP (+), while lane 2 does not (−). Lanes 4 to 7 contain a 6 mM concentration of the indicated divalent cation salt. Reaction mixtures were fractionated on a 5% acrylamide–Tris-borate-EDTA gel, dried, and exposed to a PhosphorImager plate.