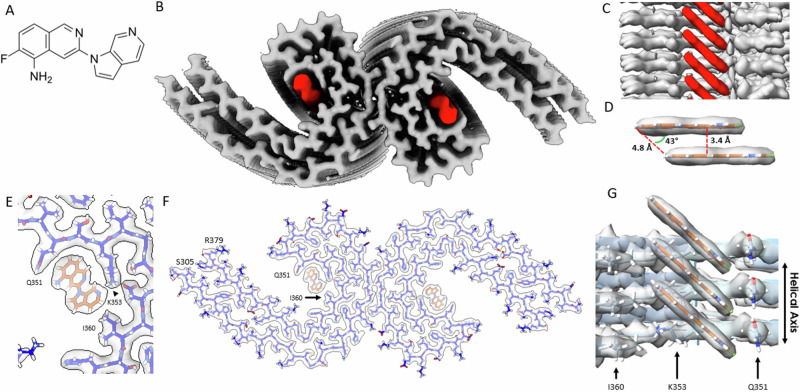
Fig. 1. Structure of MK-6240 bound to tau PHF.
A Molecular structure of MK-6240. B Cryo-EM map of AD tau PHFs (Grey) with bound MK-6240 (Red). C Side-view depiction of MK-6240 (red) situated within the binding pocket of the cleft within the AD tau PHF (Grey). MK-6240 adopted a stacked arrangement perpendicular to the fibril axis. One MK-6240 molecule spanned approximately two tau monomer rungs. D Isolated atomic representation of MK-6240 with its binding orientation. Peripheral atoms (alpha-carbon Hydrogen, left; and Fluorine, right) exhibit a 4.8 Å distance between them. Between heterocycles or parallel atoms within MK-6240 molecules, a ~ 3.3 Å distance is observed. E Close-up depiction of the binding site, accentuating the proximity of the three amino acids (Q351, K353, and I360) to MK-6240. F Atomic model showcasing the MK-6240 binding site on paired helical filaments. Cryo-EM density (white) is juxtaposed with the atomic model of the tau fold (blue) and MK-6240 (orange). G Side-view, zoomed-in perspective (from within the cleft) of the MK-6240 binding site, revealing the ~1:1 stoichiometry and the angle that aligns individual MK-6240 molecules with both themselves and the filament axis.