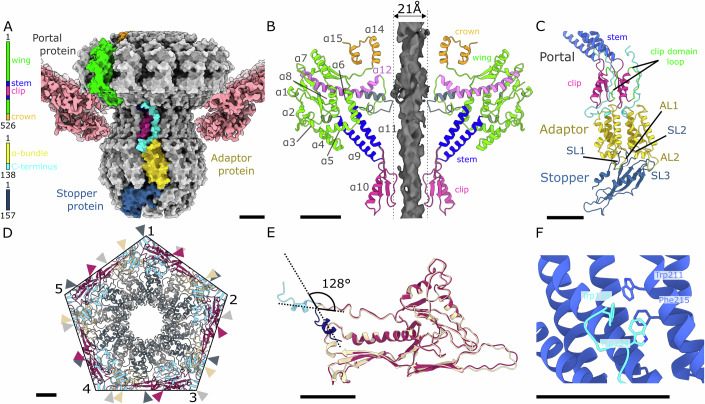
Figure 3. Structure of JBD30 connector complex.
(A) Molecular surface representation of JBD30 connector composed of a dodecamer of portal proteins, dodecamer of adaptor proteins, and hexamer of stopper proteins. The cryo-EM density of capsid proteins surrounding the connector complex is shown in surface representation in pink. One subunit of each of the connector proteins is coloured according to the domain diagrams on the left of the panel. (B) Portals of virion and empty particle differ in the structure of wing domain helix α12. Cartoon representation of two opposite portal proteins from a virion coloured according to domains (as in panel (A)). Portal proteins from an empty particle are depicted in grey. Helix α12 is fully stretched in the empty particle and the tunnel loop narrows the portal channel to 21 Å. (C) Symmetry reduction from twelvefold of the adaptor and sixfold of the stopper complex. The α-helical bundles of two adjacent adaptor proteins sit on stopper protein loops SL1, SL2, and SL3. Loops AL1 and AL2 of the adaptor protein reach over the stopper protein rim. The C-terminus of the adaptor protein runs through the cleft between the clip domains of two adjacent portal proteins. Cartoon representations of portal, adaptor, and stopper proteins are coloured according to domains as in panel (A). The clip domain loops that intertwine between the neighbouring portal proteins are highlighted in green. (D) Symmetry mismatch between capsid and portal. The capsid–portal interface is viewed along the tail axis from the outside of the particle. The portal proteins are shown in alternating grey and dark grey, the major capsid proteins are coloured in alternating purple and beige, the minor capsid proteins are shown in light blue. Positions of individual portal and major capsid proteins are indicated by arrows. (E) Superimposition of cartoon representations of major capsid protein interacting with another capsomer (beige and N-terminus in dark blue) and capsid protein adjacent to portal dodecamer (purple and N-terminus in light blue) and one showing the bending of the N-terminal arm which enables incorporation of the portal complex into the capsid. (F) Interactions between portal protein stem domain (blue) and adaptor protein C-terminal hook (cyan). Side chains of the interacting residues are shown in stick representations. Scale bars represent 25 Å.