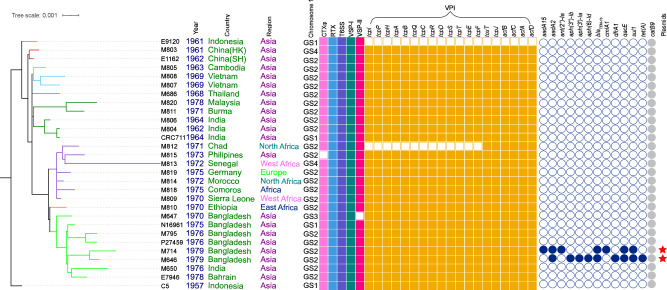
Fig. 1. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of the complete genomes of the early seventh pandemic (1961–1979).
The tree was rooted using V. cholerae strain C5 as an outgroup. The metadata is noted on the right side of the tree. Genome rearrangement structures of chromosome 1 are marked as GS1-GS4 (see Supplementary Fig S5 for details). Filled and empty squares represent gene presence and absence of virulence factors or genes shown respectively: the cholera toxin (CTXφ), the Vibrio pathogenicity island (VPI), Vibrio seventh pandemic islands (VSP-I and VSP-II), type VI secretion system (T6SS) and the repeats-in-toxin (MARTX) toxin (RTX). Filled circles represent the presence of an antibiotic resistance gene as listed. catB9 is annotated in grey since it has not been associated with phenotypic resistance. Red stars denote the two new IncA/C plasmids. The colours of the branches correspond to the clusters identified in Fig. 2 (see Fig. 2 for details). Other colours in different columns were for visual separation purposes.