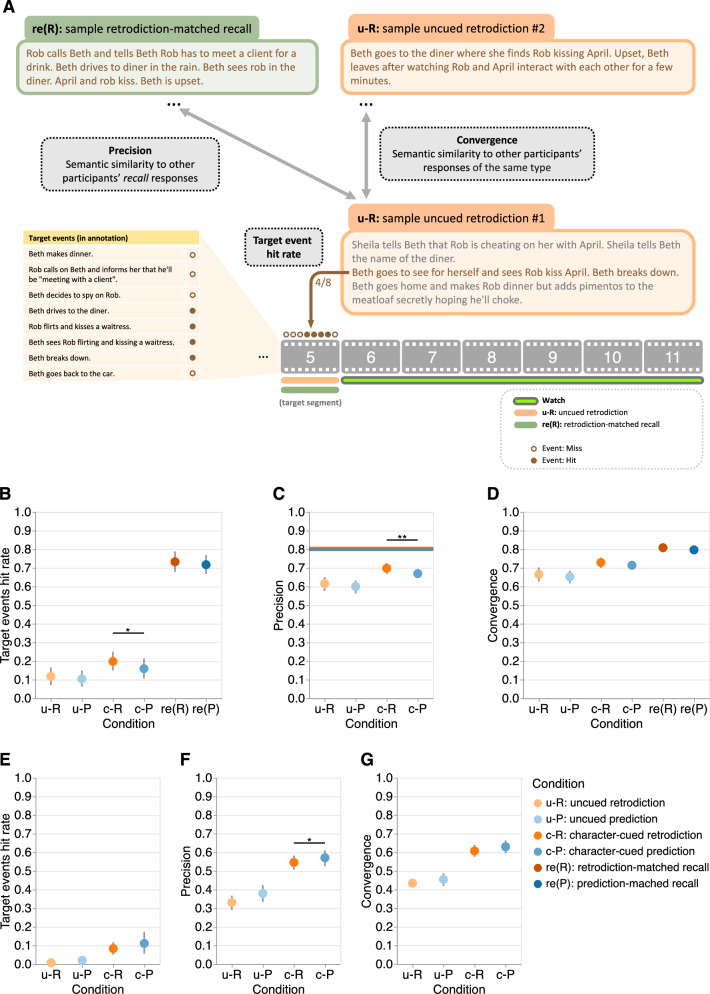
Fig. 3. Retrodiction, prediction, and recall performance on target segments by experimental condition in our main and replication experiments.
A Methods schematic. For each retrodiction, prediction, and recall response, we calculated the hit rate for events in the target segment (see Response analyses), the response precision (see Text embeddings of participants' responses), and the response convergence across participants. B Target event hit rate (main experiment). Mean proportions of target events that were contained in participants' (n = 36) responses, for each response type, averaged across target segments (n = 20). Linear mixed models revealed no statistically significant difference between uncued retrodictions and predictions (p = 0.729), and higher target event hit rates in character-cued retrodictions than predictions (p = 0.032). C Response precision (main experiment). Mean precisions of participants' responses, for each response type, averaged across target segments. The horizontal lines denote the mean pairwise semantic similarities (see Text embeddings of participants' responses) across recall responses (re(R): orange; re(P): blue). Linear mixed models revealed no statistically significant difference between uncued retrodictions and predictions (p = 0.287), and higher response precision in character-cued retrodictions than predictions (p = 0.007. D Response convergence (main experiment). Mean (across-participant) convergence of participants' responses, for each response type, averaged across target segments. Linear mixed models revealed no statistically significant difference between uncued retrodictions and predictions (p = 0.464), and no statistically significant difference between character-cued retrodictions and predictions (p = 0.163). E Target event hit rate (replication experiment). Mean proportions of target events that were contained in participants' (n = 37) responses, for each response type, averaged across target segments (n = 12). Linear mixed models revealed no statistically significant difference between uncued retrodictions and predictions (p = 0.054), and no statistically significant difference between character-cued retrodictions and predictions (p = 0.533). F Response precision (replication experiment). Same format as Panel (C). Linear mixed models revealed no statistically significant difference between uncued retrodictions and predictions (p = 0.083), and lower response precision in character-cued retrodictions than predictions (p = 0.032). G Response convergence (replication experiment). Same format as Panel (D). Linear mixed models revealed no statistically significant difference between uncued retrodictions and predictions (p = 0.592), and no statistically significant difference between character-cued retrodictions and predictions (p = 0.097). All panels: error bars denote bootstrapped 95% confidence intervals. Asterisks indicate significance in the (generalized) linear mixed models: * denotes p < 0.05, and ** denotes p < 0.01.