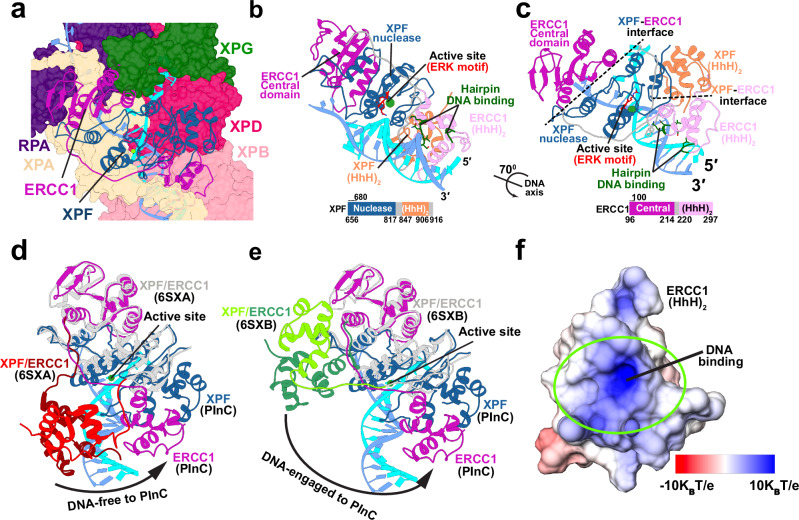
Fig. 3. XPF/ERCC1 is positioned for precise incision at the 5′ DNA junction.
a View of XPF/ERCC1 at the 5′ junction. ERCC1 and XPF are depicted in cartoon representation and colored in magenta and dark blue, respectively. The damaged and undamaged DNA strands are shown in cyan and light blue, respectively. b View of the XPF/ERCC1 heterodimer interacting with DNA at 5′ junction. The ERK active site motif in shown explicitly and colored in red. XPF and ERCC1 are colored by domain. A schematic representation of the XPF and ERCC1 sequences, indicating the domains, is shown below. c View of the XPF/ERCC1 heterodimer rotated by 70° around the dsDNA axis. d Conformational shift of XPF/ERCC1 relative to the DNA-free XPF/ERCC1 structure (6SXA). e Conformational shift of XPF/ERCC1 relative to the DNA-engaged XPF/ERCC1 structure (6SXB). The XPF nuclease and ERCC1 central domains are overlayed for comparison. The XPF/ERCC1 (HhH)2 domains are colored in red and dark red in the DNA-free structure and green and dark green in the DNA-engaged structure. ERCC1 and XPF in the PInC are colored in magenta and blue, respectively. f Electrostatics of the ERCC1 (HhH)2 DNA-binding surface. The electrostatic potential is mapped onto the molecular surface and colored from red (negative) to blue (positive).