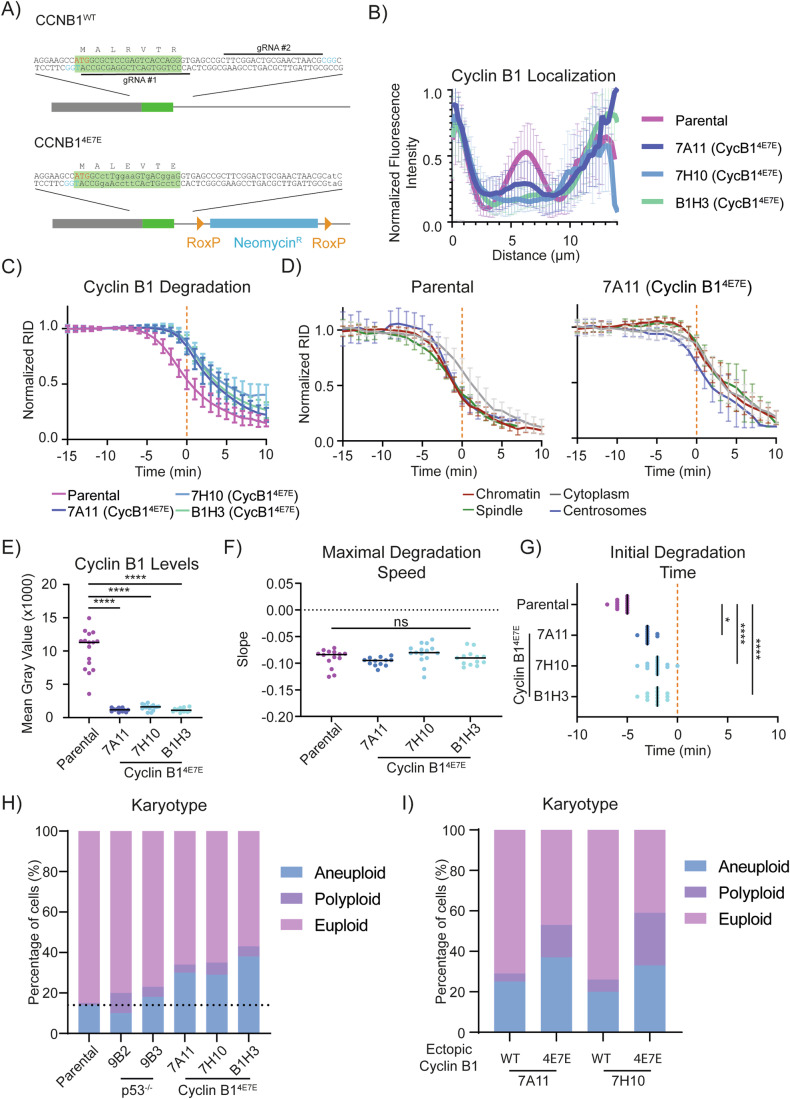
Figure 7. Endogenous Cyclin 4E7E recapitulates ectopic Cyclin 4E7E and increases genomic instability.
(A) Schematic representation of the CRISPR strategy used to introduce the 4E7E mutation. The green box indicates CyclinB1’s first exon, the blue box is a neomycin resistance cassette, grey box indicates the 5’UTR of CyclinB1. Yellow triangles indicate RoxP sites. The red text refers to CyclinB1’s ATG, blue text refers to PAM sites. (B) Graphs representing the pixel-by-pixel fluorescence intensity over a line going from centrosome to centrosome of RPE-1 Cyclin B1-mEmerald+/+ compared to Cyclin B14E7E clones. For (panels B–G): n ≥ 12 cells per condition, N = 3 independent experiments. Mean ± standard deviation are plotted. (C, D) Cyclin B1 degradation graph representing the fluorescence intensity of Cyclin B1 over time of RPE-1 Cyclin B1-mEmerald+/+ compared to Cyclin B14E7E clones. Mean ± standard deviation are plotted. (E) Dot plots representing the quantification of the mean fluorescence intensity of Cyclin B1 during metaphase in RPE-1 Cyclin B1-mEmerald+/+ compared to Cyclin B14E7E clones. (F, G) Dot plots representing the maximal degradation speed (E) or the initial degradation time (F) of RPE-1 Cyclin B1-mEmerald+/+ compared to Cyclin B14E7E clones. (H) Bar graph representing the karyotype classification from metaphase chromosome spreads of RPE-1 Cyclin B1-mEmerald+/+ compared to p53−/− clones and Cyclin B14E7E clones. The dotted line represents the level of aneuploidy in parental cells. N = 3 independent experiments. (I) Bar graph representing the karyotype classification from metaphase chromosome spreads of the indicated RPE-1 Cyclin B14E7E-mEmerald+/+ clones following 3 weeks of ectopic expression of either Cyclin B1WT-mScarlet or Cyclin B14E7E-mScarlet. N = 2 independent experiments. Source data are available online for this figure.