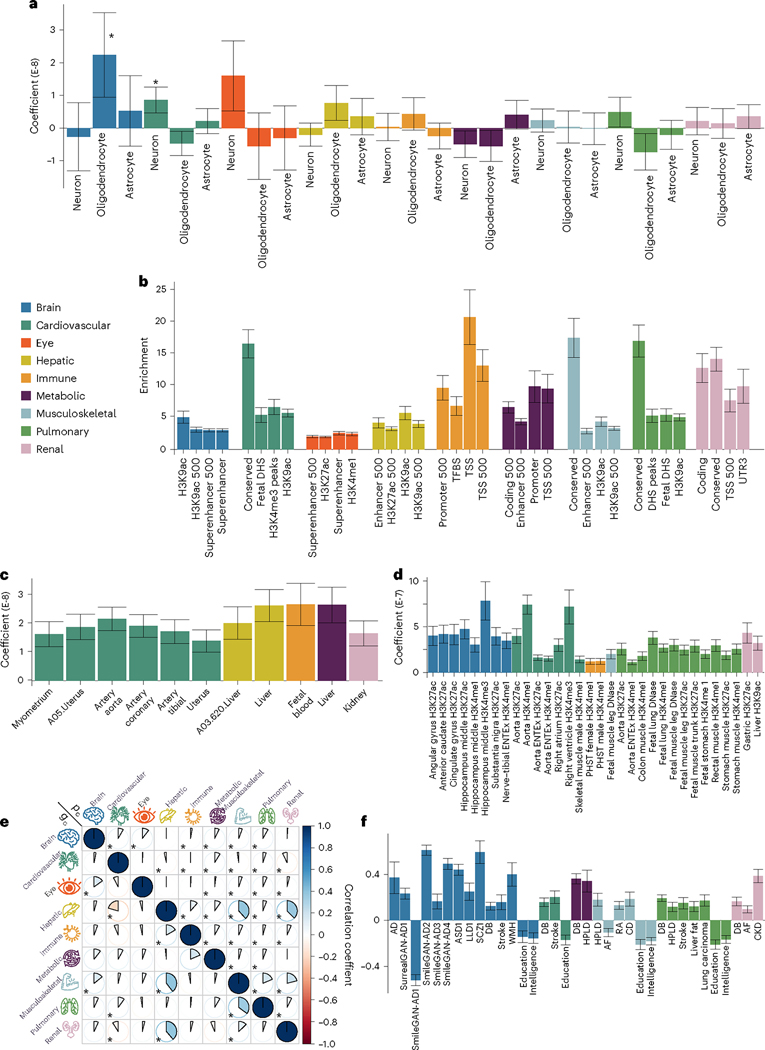
Fig. 5 |. Partitioned heritability enrichment and genetic correlation of the nine BAGs.
a, Cell-type-specific partitioned heritability estimates for neurons, oligodendrocytes and astrocytes. b, Partitioned heritability estimates for the general 53 functional categories. For visualization purposes, we only show the four categories with the highest significant estimates for each BAG. The label for 500 denotes a 500-base pair window around each of the 24 main annotations in the full baseline model, which prevents a biased estimate inflated by heritability in flanking regions83; TSS, transcription start site; DHS, DNase I hypersensitivity site; TFBS, transcription factor binding site. c, Tissue-specific partitioned heritability estimates using gene sets from multitissue gene expression data. d, Tissue- and chromatin-specific partitioned heritability estimates using multitissue chromatin data. e, Cheverud’s conjecture: the genetic correlation between two BAGs (gc; bottom triangle) mirrors their phenotypic correlation (pc; top triangle). f, Genetic correlations between the nine BAGs and 41 clinical traits, including chronic diseases and their subtypes involving multiple human organ systems, education, intelligence and reaction time. An asterisk (*) denotes Bonferroni-corrected significance, and the absence of an asterisk indicates that all results remain significant after correction. For a–d and f, the standard error of the estimated parameters is presented using error bars. The measure of the center for the error bars represents the inferred statistics. The sample sizes, P values and other detailed statistics are presented in Source Data Files 13–18 and Supplementary Table 5; all P values are two sided; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; ASD, autism spectrum disorder; LLD, late-life depression; SCZ, schizophrenia; DB, type 2 diabetes; WMH, white matter hyperintensity; HPLD, hyperlipidemia; AF, atrial fibrillation; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; CD, Crohn’s disease; CKD, chronic kidney disease; PHST, primary hematopoietic stem cell.