Fig 1.
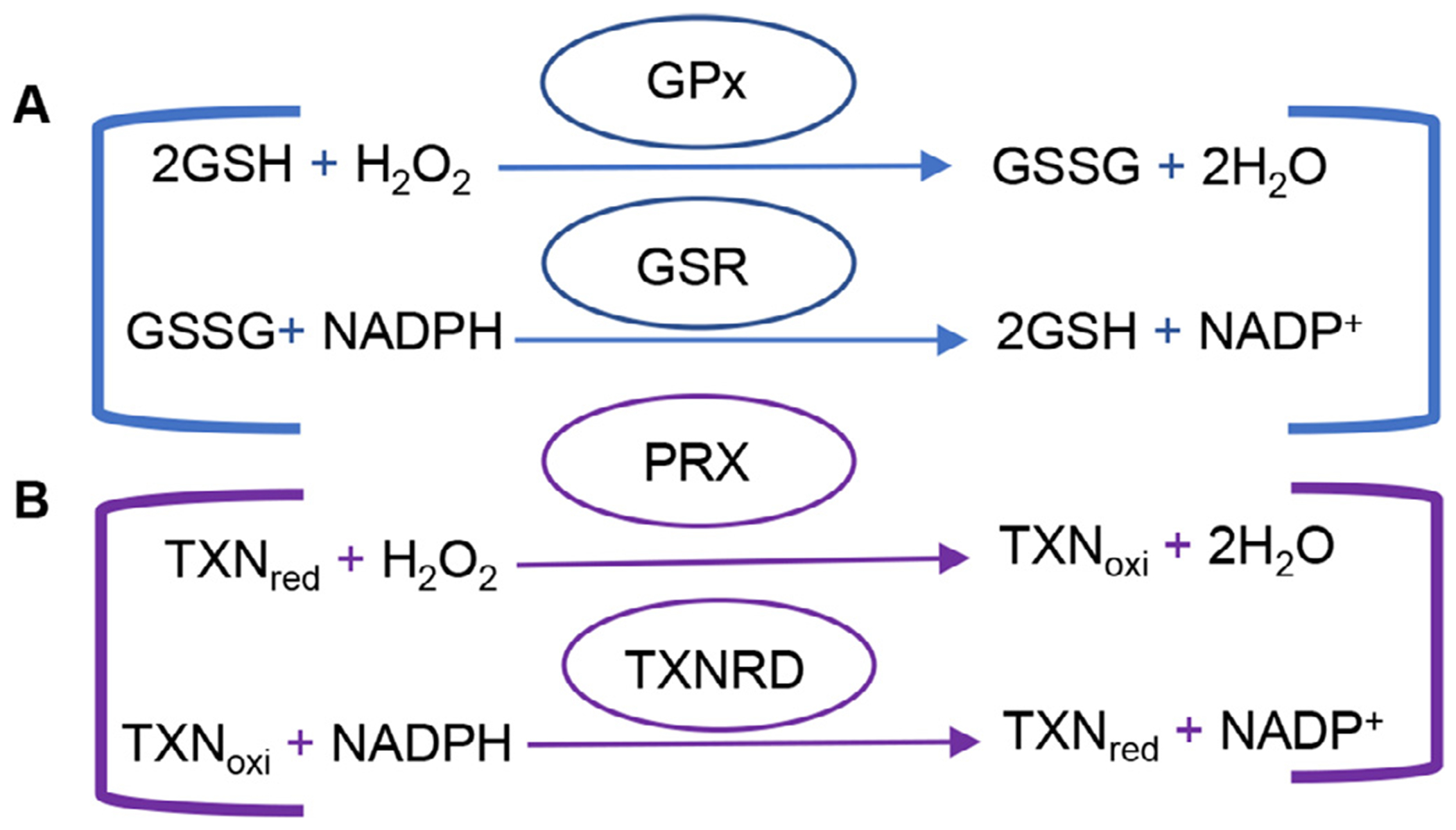
Glutathione and thioredoxin antioxidant defense systems. (A) Reduced glutathione functions in quenching radicals, maintaining thiol groups, serving as a co-enzyme for glutathione peroxidase and maintaining cellular redox homeostasis. GPx reduces H2O2 to H2O while oxidizing GSH to GSSG. GSR then uses NADPH as a co-factor to form -SH groups in proteins that interact with the reduction of GSSG to GSH. (B) Thioredoxin reduces H2O2 and protein disulfide, in protein repair and DNA synthesis, regulating transcription factors and apoptosis, and in immunomodulation. PRX reduces H2O2 to H2O while oxidizing reduced thiore-doxin. NADPH-dependent TXNRD then catalyzes the reduction of oxidized thioredoxin. GPx=glutathione peroxidase, GSH = reduced glutathione, GSSG = oxidized glutathione, GSR = glutathione reductase, NADP = reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, PRX = peroxiredoxin, TXNRD = thioredoxin reductase
